AWS Load Balanced
You can configure Posit Workbench to run on multiple servers using an external database and a networked file system. Workbench is hosted on each server, and user sessions are distributed across servers to divide the load. Using external components is required for a load-balanced implementation, providing a robust architecture that is in line with the best practices and existing processes of many organizations. This architecture also offers flexibility to scale up in the future without needing to migrate the database or application files.
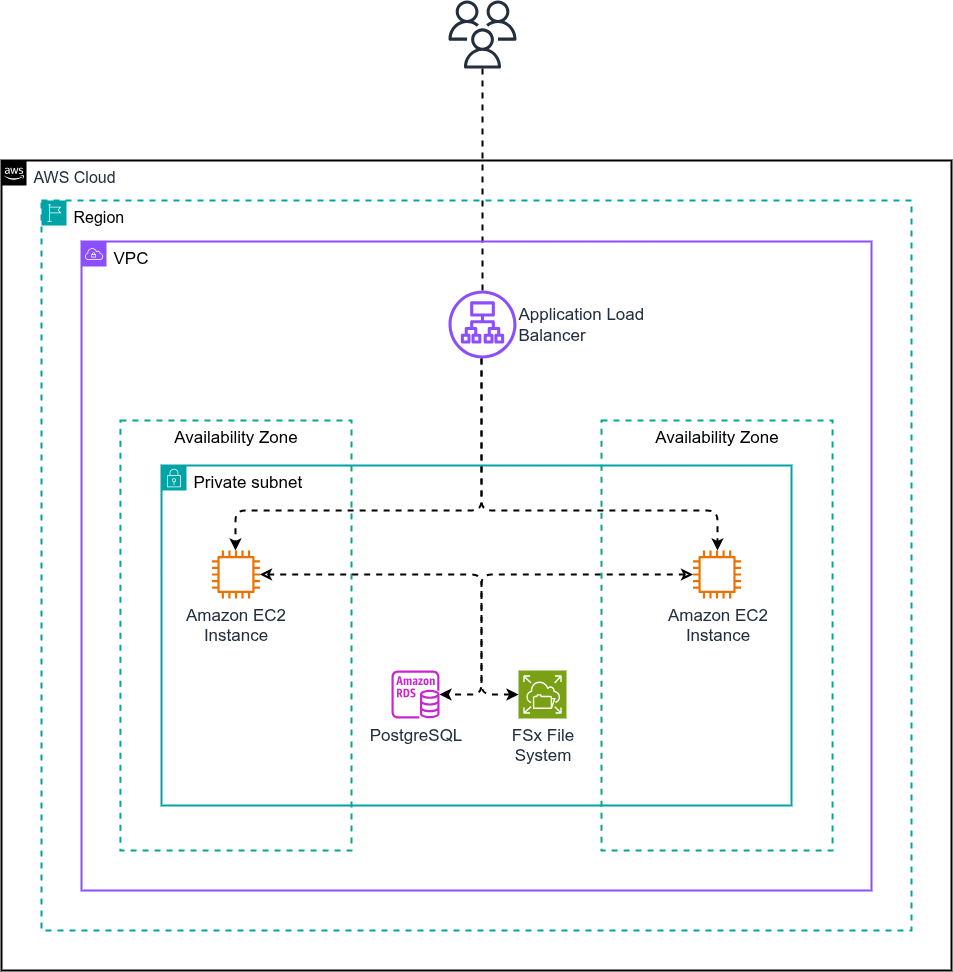
Architectural overview
This architecture uses the following components:
- Two or more AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances running Workbench, possibly divided across Availability Zones
- AWS Relational Database Service (RDS) for PostgreSQL, serving as the application database
- Amazon FSx using either OpenZFS or Lustre, to provide a networked file system to store file data
Architecture diagram
Sizing and performance
The performance of this architecture is dictated by EC2 type and the CPU and RAM characteristics of the Workbench instances, and the performance of the attached RDS database and FSx file system.
A more detailed overview on node sizing can be found in the Architecture considerations section.
Nodes
Ensure the EC2 instances are large enough to handle peak usage. The size and type of instance depend on the needs and workloads of end users. For the best experience, estimate the number of concurrent sessions expected and the compute resources required for each session, focusing on CPU and memory. Choose an instance type that supports the largest size of session that will be run. A typical configuration deploys enough instances to spread a typical number of concurrent sessions so that each instance handles two or three such sessions.
CPU
Workbench alone consumes only a small amount of system resources. However, when estimating needs, reserve two to six cores for Workbench itself, in addition to accounting for the Python and R processes running in user sessions or Workbench Jobs. Review the considerations in the Number of users section to estimate the total number of CPU cores needed.
RAM
User sessions and Workbench Jobs consume memory. The number of users and how they typically work with their data dictate the amount of memory needed. Review the Memory and disk requirements section to estimate the amount of memory needed.
Database
This configuration requires a PostgreSQL database for the Workbench product database. This configuration puts little stress on the database. Up to 5,000 concurrent sessions with a db.t3.micro instance have been tested with no notable performance degradation.
Storage
For this architecture, we recommend FSx for OpenZFS or FSx for Lustre. We do not recommend Regional EFS or Single Zone EFS, as these file systems may encounter performance issues.
When considering which FSx file system to use:
- FSx for OpenZFS offers lower latency and can be deployed in multiple Availability Zones to increase system resiliency. Because it does not support extended POSIX ACLs, FSx for OpenZFS does not support Workbench Project Sharing.
- FSx for Lustre offers higher maximum capacity and potentially higher bandwidth, but it is not available in multiple Availability Zones. Choose FSx for Lustre if you want to use Workbench Project Sharing.
The Workbench file system usage for configuration and state storage is modest, likely less than a few GB for a production system. Therefore, the size of your FSx volume depends almost entirely on end-user usage patterns. Some data science teams store very little in their home directories and only need a few GB per person. Other teams may download large files into their home directories and need much more. Administrators should consult with their user groups to determine the appropriate size.
FSx for Lustre volumes are provisioned in 1.2 TB chunks. This amount can be shared across all user home directories, Workbench configuration, and Workbench state storage.
For more information on the differences between file systems, please refer to the Cloud-specific recommentations in the Posit Team Storage documentation.
Load balancer
This architecture utilizes an AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) in order to provide public ingress to the Workbench instances. Additional Workbench instances can be added as needed to improve resiliency and reduce load.
Configuration details
Networking
The architecture is implemented in a virtual private cloud, utilizing both public and private subnets. The RDS database instance, the FSx file systems, and the EC2 instance are located within the private subnets, and ingress to the EC2 instances are managed through an ALB.
Resiliency and availability
This architecture includes Workbench in at least two replicas configured in a load-balanced setup, making it resilient to failures of one instance. If configured using multiple Availability Zones, this architecture is resilient to a failure of an Availability Zone that does not contain the database.