Operational Metrics
This section describes the configuration and management of operational and usage metrics, of which there are three categories:
- Metrics describing resource usage over time (trends) are enabled with the
Metrics.Enabledsetting. - Prometheus metrics can be turned on by using the setting
Metrics.PrometheusListenOmitting the setting or configuring it to a blank value will turn off the Prometheus endpoint. - More discrete usage events are enabled with the
Metrics.Instrumentationsetting.
Both resource usage trends and instrumentation metrics are set to true by default. Prometheus metrics can be configured using the information outlined in the Prometheus Metrics section below.
Resource metrics
Posit Connect uses a separate rserver-monitor process to record resource (CPU, memory, etc.) usage over time. These metrics are collected by default, but the customization settings described in the remainder of this section have no effect when Metrics.Enabled is off.
Resource metrics settings
Metrics data is written by default to a set of RRD files. This data is stored by default at /var/lib/rstudio-connect/metrics. You can specify an alternate data path by using the Metrics.DataPath setting.
The rserver-monitor process runs (by default) with the same user account Connect uses to run its processes associated with deployed content. By default, this user account is rstudio-connect (see the Applications.RunAs setting). You can specify an alternate user account for the rserver-monitor process by modifying the Metrics.User setting.
Posit Connect also supports logging of metrics to Graphite, and it supports disabling its default behavior of logging to RRD. Please see the Metrics configuration appendix for more options for configuring the resource metrics in Connect.
Resource metrics process management
Connect automatically spawns a process (rserver-monitor) to help maintain resource data. If this process exits, Connect will restart it in an attempt to record as much resource information as possible. Connect will delay restarting rserver-monitor if it observes rapid, repeated failures.
Since the rserver-monitor needs permission to write data to the metrics data directory, Connect attempts to ensure the necessary permissions at startup. When Connect starts, it grants ownership of the metrics data directory to the user account that will be used to start rserver-monitor.
Resource metrics process logging
The rserver-monitor process logs its output to syslog. If the process is unable to run, you can check the system log (e.g., /var/log/messages or /var/log/syslog) for messages.
Per-content job metrics
Connect can collect resource metrics (CPU, memory, and connection counts) for individual content jobs. These metrics are specific to each job execution in contrast to the server-wide resource metrics. Publishers can view these individual content job metrics alongside job logs in the Connect dashboard.
By default, publishers must enable these job metrics for individual content items using the content settings on the Connect Dashboard, or via the metrics_collection_enabled field in the content API. To enable per-job metrics collection for all jobs by default, set Applications.MetricsCollectionEnabled to true:
/etc/rstudio-connect/rstudio-connect.gcfg
[Applications]
MetricsCollectionEnabled = trueUsage events
Posit Connect can record event-style usage information which is intended to answer questions like, “Who used my Shiny app and for how long?” This information is stored in dedicated tables in the database. When using SQLite, this is handled automatically by creating a second database file named connect-instrumentation. For PostgreSQL, a second, full database URL can be provided in the Postgres.InstrumentationURL setting. If it is not specified, it will default to the value of Postgres.URL. This allows you to store the event data in the same place as the rest of the Connect information, in a different schema, or even a different database, whichever meets your needs best. Please see the PostgreSQL section for more details about using PostgreSQL.
Content that has been locked does not record new views.
There is currently no data retention policy so all data will always be kept. Data retention controls will be added in a future release.
Shiny application events
When a user opens a Shiny application, an event containing their user information and the length of their session will be logged to the instrumentation database. It’s important to note that some configuration settings may affect how the ending time for a session is set.
The ended time will always include the duration configured in the
Client.ReconnectTimeoutproperty. This is 15 seconds, by default.The
Scheduler.ConnectionTimeoutandScheduler.ReadTimeoutvalues control when an idle session is terminated by Posit Connect. This will, as a side effect, set the ended time for the session.
These events may be retrieved by making use of the “Get Shiny Application Usage” API. The API returns information in pages and provides URLs in each response that may be used as-is to request the next or previous page of information. All data may be retrieved by first invoking the endpoint without next or previous parameters to return the first page of results and then repeatedly following the next link in each response until that link becomes null.
The API may only be used by administrators and publishers. Additionally, publishers may only retrieve information about the Shiny apps that they own.
Optional filters within the request may be used to limit what usage records are returned with each response. Filters are “ANDed” together (i.e. data returned will satisfy all filters).
Application GUIDs may be provided to limit responses to particular applications. A publisher will be implicitly limited to only applications he or she owns. If a publisher asks for information about other content (content owned by someone else), the result will not contain data for that application and will not be reported as an error.
Timestamps may be provided to limit usage information to a more narrow time window of interest. By using the from or to filters, either independently or together, the information returned will be limited to applications that were being accessed within that window of time. It’s worth noting that information for an app will be included in such a request if any portion of its usage by a user falls within the specified time window.
The data returned for a Shiny application session includes a version number. As the Connect software has evolved, issues have been identified with how data is recorded. The version number provides an indication of any known issues and are described below.
| Version | Issue |
|---|---|
| 0 | Extraneous records were recorded under some conditions, notably when protocols other than websockets were used. These can be identified by the same value for started and ended. This may adversely affect analyses involving counts or session lengths. |
| 1 | No known issues. |
The min_data_version filter may be used to control what data to return. The default minimum data version to return is 1.
Example recipes are available in the Cookbook.
Content visit events
When a user visits any content type other than a Shiny application, an event is logged to the instrumentation database noting the time of the visit, the visitor and the content visited.
Content that has been locked does not record new views.
Requests made to APIs are also recorded as content visit events. Dashboard and open solo visits to APIs may record a hit for the content visit as well as the serving of documentation, depending on how your API is configured. For example, open solo visits to Plumber Swagger documentation and Plumber Swagger example executions are not recorded, but FastAPI serving documentation when a root GET / is not provided counts as a valid visit.
Visit events are written to the database when the number of hits reaches the configured value of Metrics.InstrumentationBatchSize (default 200) or the elapsed time reaches the configured value of Metrics.InstrumentationInterval (default 2s). In the event the Connect process exits or is terminated, those values bound the amount of queued instrumentation data that will not be stored. If needed, you can restore the old immediate-write behavior by configuring Metrics.InstrumentationBatchSize = 1.
These events may be retrieved by making use of the “Get Content Visits” API. The API returns information in pages and provides URLs in each response that may be used as-is to request the next or previous page of information. All data may be retrieved by first invoking the endpoint without next or previous parameters to return the first page of results and then repeatedly following the next link in each response until that link becomes null.
The API may only be used by administrators and publishers. Additionally, publishers may only retrieve information about the content that they own.
Optional filters within the request may be used to limit what visit records are returned with each response. Filters are “ANDed” together (i.e. data returned will satisfy all filters).
Application GUIDs may be provided to limit responses to particular content. A publisher will be implicitly limited to only content he or she owns. If a publisher asks for information about other content (content owned by someone else), the result will not contain data for that content and will not be reported as an error.
Timestamps may be provided to limit visit information to a more narrow time window of interest. By using the from or to filters, either independently or together, the information returned will be limited to content that was visited within that window of time.
The data returned for a visit to content includes a version number. As the Connect software has evolved, issues have been identified with how data is recorded. The version number provides an indication of any known issues and are described below.
| Version | Issue |
|---|---|
| 0 | Extraneous records were recorded under some conditions, notably when content is not rendered to a self-contained page and refers to images, CSS, JavaScript, and the like as files external to the page but within the content. |
| 1 | Activity to Plumber APIs and Python applications and APIs was under-counted. Visits were not recorded when the content was hosted within the Posit Connect dashboard. |
| 2 | Dashboard visits to Plumber, Voila, Dash, Streamlit, and Bokeh content were over-counted. |
| 3 | No known issues. |
The min_data_version filter may be used to control what data to return. The default minimum data version to return is 3.
Example recipes are available in the Cookbook.
Prometheus metrics
Posit Connect supports the use of the monitoring and alerting system Prometheus via a publicly available metrics endpoint. The Prometheus listen port is configurable via the Metrics.PrometheusListen setting.
Example configuration:
/etc/rstudio-connect/rstudio-connect.gcfg
[Metrics]
PrometheusListen = ":3232"To explicitly turn Prometheus metrics off, set Metrics.PrometheusListen to an empty string:
/etc/rstudio-connect/rstudio-connect.gcfg
[Metrics]
PrometheusListen = ""Prometheus collectors configuration
By default, when Prometheus metrics are enabled, all metric collectors are enabled. You can selectively disable individual collectors using the following configuration options:
/etc/rstudio-connect/rstudio-connect.gcfg
[Metrics]
PrometheusListen = ":3232"
; Disable specific collectors
PrometheusCollectorApplicationsEnabled = false
PrometheusCollectorBuildEnabled = false
PrometheusCollectorHTTPEnabled = false
PrometheusCollectorPlatformRuntimeEnabled = false
PrometheusCollectorQueueEnabled = falseThe available collector configuration options are:
Metrics.PrometheusCollectorApplicationsEnabled- Controls application/content usage and health metrics. Defaults totruewhen Prometheus is enabled.Metrics.PrometheusCollectorBuildEnabled- Controls static build metadata (version, vcs, build date). Defaults totruewhen Prometheus is enabled.Metrics.PrometheusCollectorHTTPEnabled- Controls HTTP metrics (latency, size, codes, route labels). Defaults totruewhen Prometheus is enabled.Metrics.PrometheusCollectorPlatformRuntimeEnabled- Controls Go runtime and OS process metrics (GC, memory, goroutines, CPU, file descriptors). Defaults totruewhen Prometheus is enabled.Metrics.PrometheusCollectorQueueEnabled- Controls queue/scheduler metrics (throughput, durations, backlog). Defaults totruewhen Prometheus is enabled.
The Metrics.HTTPRequestLatencyEnabled setting is deprecated in favor of Metrics.PrometheusCollectorHTTPEnabled and will be removed in a future release.
Included metrics
The following metrics are exposed publicly at <your-connect-server>:<prometheus-port>/metrics. See the Prometheus documentation for more information on metric types.
Active users metrics
| Label | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connect_users_active | gauge | Count of distinct active users over various time windows. An active user is an unlocked user with recorded activity within the specified time window. Labeled with window (time period: 24h, 7d, 30d, or 1y) and role (account type: administrator, publisher, or viewer). Downstream systems can aggregate across roles to get totals per time window. |
Application metrics
These metrics are controlled by Metrics.PrometheusCollectorApplicationsEnabled:
| Label | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connect_content_app_sessions_current | gauge | Active content sessions are totalled and returned per user. The content and user identifiers are in GUID format. Content being accessed anonymously has a user value of unknown. An active session means a user currently has an open connection to the application. This metric is only tracked and reported for Shiny applications. |
| connect_content_hits_total | counter | Visits to all content items are totalled and returned per user. The content and user identifiers are in GUID format. Shiny content being accessed anonymously has a user value of unknown. |
Queue metrics
These metrics are controlled by Metrics.PrometheusCollectorQueueEnabled:
| Label | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue | gauge | The total number of jobs (scheduled reports render, jobs finalizer, LDAP membership updater, and Git updater) in the jobs queue. |
| connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds | gauge | The age of the oldest job in the jobs queue. |
| connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds | gauge | The duration that an active job from the queue has been running for. |
HTTP metrics
When OpenTelemetry API instrumentation is enabled (OpenTelemetry.Enabled = true and OpenTelemetry.APIInstrumentation = true), the connect_http_* metrics listed below are automatically disabled and replaced by OTel-standard http.server.* metrics. See Migrating from legacy Prometheus HTTP metrics for a mapping table and migration guidance.
These metrics are controlled by Metrics.PrometheusCollectorHTTPEnabled:
| Label | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connect_http_request_inflight_gauge | gauge | Number of HTTP requests currently being processed. |
| connect_http_request_count | counter | Total number of HTTP requests processed. Labeled by method, route, and response code. |
| connect_http_request_duration_seconds | histogram | HTTP request/response duration in seconds. Labeled by method, route, and response code. |
| connect_http_request_size_bytes | histogram | HTTP request size in bytes. Labeled by method, route, and response code. |
| connect_http_response_size_bytes | histogram | HTTP response size in bytes. Labeled by method, route, and response code. |
Build metrics
These metrics are controlled by Metrics.PrometheusCollectorBuildEnabled:
| Label | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| go_build_info | gauge | Build information about the Connect server. Always has a value of 1. Labeled with path, version, and checksum. |
Platform runtime metrics
These metrics are controlled by Metrics.PrometheusCollectorPlatformRuntimeEnabled and include:
- Go runtime metrics: Garbage collection statistics (e.g.,
go_gc_*), memory usage (e.g.,go_memory_*), scheduler metrics (e.g.,go_sched_*) - Process metrics: CPU usage, memory usage, file descriptor usage, and process start time
See the Prometheus Go client documentation for a complete list of platform runtime metrics.
Here is an example response received from the /metrics endpoint:
# HELP go_build_info Build information about the main Go module.
# TYPE go_build_info gauge
go_build_info{checksum="",path="connect",version="(devel)"} 1
# HELP connect_http_request_inflight_gauge HTTP request in-flight gauge.
# TYPE connect_http_request_inflight_gauge gauge
connect_http_request_inflight_gauge 2
# HELP connect_http_request_count HTTP request counter.
# TYPE connect_http_request_count counter
connect_http_request_count{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content"} 145
connect_http_request_count{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/users"} 23
connect_http_request_count{code="404",method="GET",route="/v1/content"} 3
# HELP connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds The duration, in seconds, that an active job from the queue has been running for.
# TYPE connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds gauge
connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds{job_hostname="connect",queue_name="default"} 46.803664925
connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds{job_hostname="connect",queue_name="git"} 47.190667134
connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds{job_hostname="connect",queue_name="job-finalizer"} 0
connect_jobs_queue_active_job_duration_seconds{job_hostname="connect",queue_name="memberships"} 0
# HELP connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds The age in seconds of the oldest job currently in the queue
# TYPE connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds gauge
connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds{queue_name="default"} 195.45201792699999
connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds{queue_name="git"} 50.452857052
connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds{queue_name="job-finalizer"} 0
connect_jobs_queue_oldest_job_age_seconds{queue_name="memberships"} 0
# HELP connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue The total number of active jobs in the queue.
# TYPE connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue gauge
connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue{queue_name="default"} 4
connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue{queue_name="git"} 1
connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue{queue_name="job-finalizer"} 0
connect_jobs_queue_total_jobs_in_queue{queue_name="memberships"} 0
# HELP connect_http_request_duration_seconds HTTP request/response duration [seconds].
# TYPE connect_http_request_duration_seconds histogram
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.005"} 1
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.01"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.025"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.05"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.1"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.25"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="0.5"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="1"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="2.5"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="5"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="10"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content",le="+Inf"} 2
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_sum{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content"} 0.009064039
connect_http_request_duration_seconds_count{code="200",method="GET",route="/v1/content"} 2Adding a Posit Connect target to Prometheus
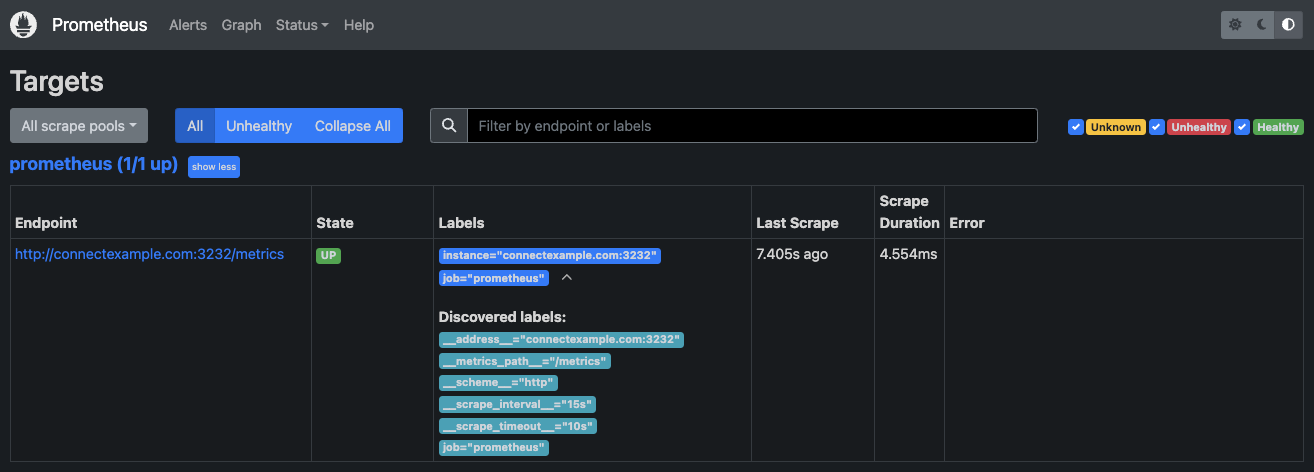
Within your Prometheus configuration YAML, add your Posit Connect server to the scrape_configs section:
/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["connectexample.com:3232"]In the above example, our Connect host has configured a Server.Address of connectexample.com and a Metrics.PrometheusListen of :3232.
Connect currently only supports HTTP connections to the Prometheus endpoint.
After making the configuration change, you can send a SIGHUP to the Prometheus process in order to reload the configuration. You should then see the endpoint being consumed on your Prometheus dashboard:
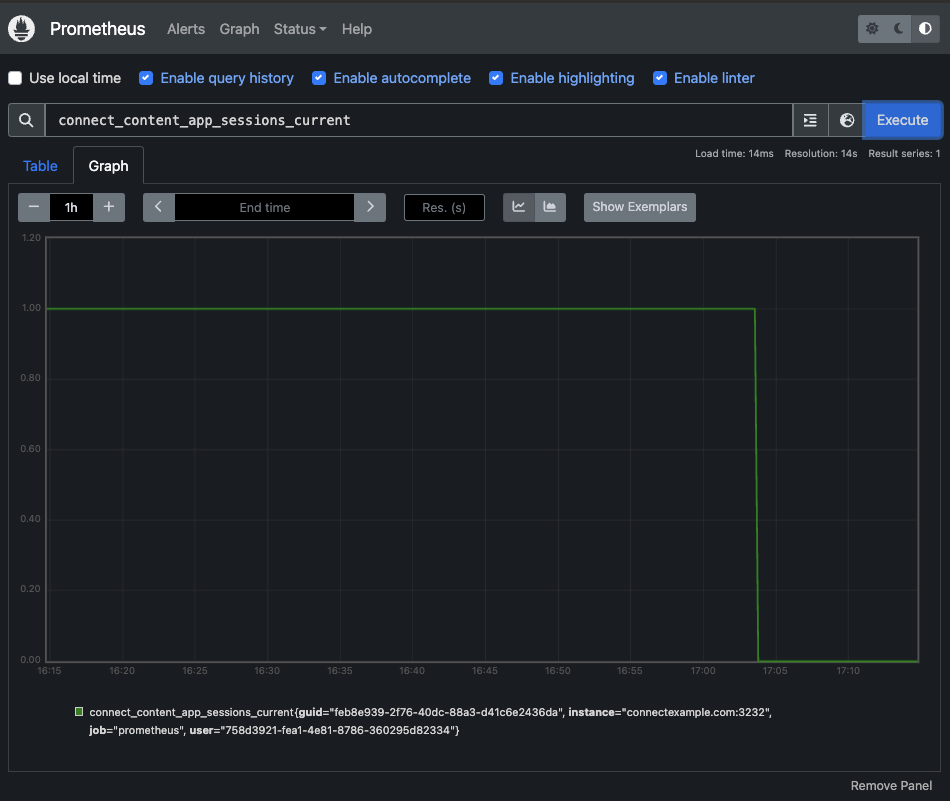
Connect data can be visualized by executing queries from the Graph tab within the Prometheus dashboard. For example, searching for connect_content_app_sessions_current displays a graph of active sessions over time:
See the Prometheus documentation for more query examples.