Custom OAuth Integrations
Workbench | Preview Enhanced Advanced
Workbench can provide user-specific OAuth credentials for sessions that integrate with any OAuth 2.0-compliant third-party service that supports the authorization code flow. These integrations allow users to securely access third-party APIs and services programmatically from Workbench sessions, where the OAuth provider is the third-party service being accessed.
This feature is designed to support standard OAuth 2.0 services; however, specific compatibility may vary across different providers.
Advantages
Using custom OAuth credentials through Workbench provides several key advantages:
- No need to manage OAuth client IDs or secrets yourself.
- Avoid hardcoding credentials in your code.
- Automatic token refresh handled by Workbench. See Automatic token refresh for details.
- Securely store and access credentials.
Authenticating with custom OAuth integrations
To use custom OAuth credentials, you must first authenticate through the Managed Credentials settings. For detailed instructions on signing in, signing out, and managing credentials, see the Managed Credentials settings section of the Managed Credentials Overview.
Once your administrator has configured custom OAuth integrations, they display in the Managed Credentials settings under Custom OAuth.
Viewing integration details
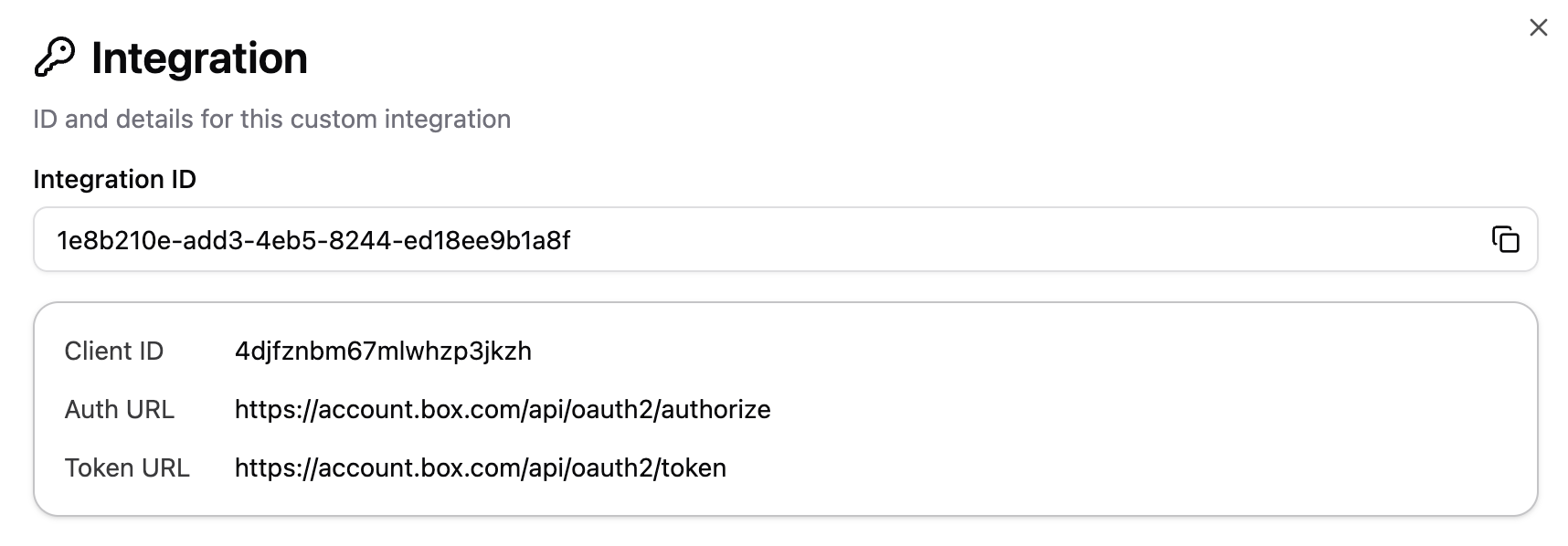
Each custom OAuth integration has an information dialog that displays important details about the integration:
- In the Managed Credentials settings, locate the integration you want to view.
- Next to the integration name, click the information icon (ⓘ).
The integration details dialog shows:
- Integration ID (GUID): The unique identifier required for programmatic access. Copy this value using the copy button to use it in your code.
- Client ID: The OAuth client identifier
- Auth URL: The OAuth authorization endpoint
- Token URL: The OAuth token endpoint
- Scopes: The permissions this integration has been granted
This information is useful for understanding what the integration can access and for programmatic use via the posit-sdk (Python) or rstudioapi (R) packages.
How custom OAuth works in sessions
Unlike advanced integrations (e.g., Databricks, Snowflake, AWS) which automatically set environment variables and create configuration files, custom OAuth integrations do not need to be selected in the New Session dialog. Once authenticated, they work differently:
- Automatic availability: Authenticated custom OAuth credentials are automatically available in all your sessions.
- Programmatic access: Access credentials through the API using the
posit-sdk(Python) orrstudioapi(R) packages. - Visibility in UI: The New Session dialog displays a list of authenticated integrations, for informational purposes only.
Using credentials in sessions
Use the posit-sdk (Python) or rstudioapi (R) package to programmatically access custom OAuth credentials. The most important operation is retrieving an access token for authenticating API requests to the OAuth provider.
To use custom OAuth credentials in your code, follow these steps:
- Get the integration ID from the Managed Credentials settings or query it programmatically using the SDK (see Finding integrations).
- Use the SDK to retrieve an access token using the integration ID.
- Use the access token in API calls to the third-party service (refer to your service’s API documentation for specifics).
Installation
To use the OAuth API, install the appropriate SDK:
pip install posit-sdkinstall.packages("rstudioapi")Getting an access token
To get an OAuth access token, you need the integration’s unique identifier (GUID). You can find this:
- In the UI by clicking the information icon (ⓘ) in the Managed Credentials settings (see Viewing integration details above)
- Programmatically using the SDK (see Finding integrations below)
An integration’s GUID is stable between sessions. A good practice is to store it as an environment variable in your project for easy access.
The integration ID can be stored as an environment variable. For example, you can use the python-dotenv package to load it from a .env file:
# .env
GITHUB_INTEGRATION_ID=a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8dfrom posit.workbench import Client
import requests
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
client = Client()
# Get credentials using the integration GUID from environment variable
integration_id = os.getenv("GITHUB_INTEGRATION_ID")
credentials = client.oauth.get_credentials(audience=integration_id)
if credentials:
access_token = credentials['access_token']
expiry = credentials['expiry']
print(f"Token expires at: {expiry}")
# Example: Use token with requests library to call GitHub API
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'}
response = requests.get('https://api.github.com/user', headers=headers)The integration ID can be stored as an environment variable. For example, you can add it to a .Renviron file in your project directory:
# .Renviron
GITHUB_INTEGRATION_ID=a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8dAfter adding the variable, restart your R session to load it:
# Get credentials using the integration GUID from environment variable
integration_id <- Sys.getenv("GITHUB_INTEGRATION_ID")
credentials <- tryCatch({
rstudioapi::getOAuthCredentials(audience = integration_id)
}, error = function(e) {
message("Failed to get credentials: ", e$message)
return(NULL)
})
if (!is.null(credentials)) {
access_token <- credentials$access_token
expiry <- credentials$expiry
cat("Token expires at:", format(expiry), "\n")
# Use token with httr2 library
library(httr2)
response <- request("https://api.github.com/user") |>
req_auth_bearer_token(access_token) |>
req_perform()
}View getOAuthCredentials() documentation or run ?rstudioapi::getOAuthCredentials in your Positron Pro / RStudio IDE R console.
OAuth tokens are sensitive credentials. Never log, print, or store tokens in plain text. Use them only for authenticated API requests.
Finding integrations
If you have not already obtained the integration GUID, you can query your available integrations to find it.
List all integrations
Retrieve all OAuth integrations configured by your administrator:
from posit.workbench import Client
client = Client()
integrations = client.oauth.integrations.find()
# Display all integrations
for integration in integrations:
print(f"{integration['name']} ({integration['guid']}): "
f"{'authenticated' if integration['authenticated'] else 'not authenticated'}")Example output:
GitHub (a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8d): authenticated
Box (1e8b210e-add3-4eb5-8244-ed18ee9b1a8f): not authenticated# Get all integrations
integrations <- rstudioapi::getOAuthIntegrations()
# Display all integrations
for (integration in integrations) {
cat(sprintf("%s (%s): %s\n",
integration$name,
integration$guid,
if (integration$authenticated) "authenticated" else "not authenticated"))
}Example output:
GitHub (a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8d): authenticated
Box (1e8b210e-add3-4eb5-8244-ed18ee9b1a8f): not authenticatedView getOAuthIntegrations() documentation or run ?rstudioapi::getOAuthIntegrations in your Positron Pro / RStudio IDE R console.
Get a specific integration
Retrieve details about a specific integration by its GUID:
# Get integration by GUID
integration = client.oauth.integrations.get("a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8d")
if integration:
print(f"Found: {integration['name']}")
print(f"Authenticated: {integration['authenticated']}")
print(f"Scopes: {', '.join(integration['scopes'])}")# Get integration by GUID
integration <- rstudioapi::getOAuthIntegration("a3c4f5d6-b8e9-4a1b-9c2d-3e4f5a6b7c8d")
if (!is.null(integration)) {
cat("Found:", integration$name, "\n")
cat("Authenticated:", integration$authenticated, "\n")
cat("Scopes:", paste(integration$scopes, collapse = ", "), "\n")
}View getOAuthIntegration() documentation or run ?rstudioapi::getOAuthIntegration in your Positron Pro / RStudio IDE R console.
Find integration by criteria
Search for integrations matching specific criteria:
# Find by name (supports regex, using anchors for exact match)
integration = client.oauth.integrations.find_by(name="^github$")
# Find authenticated integrations
integration = client.oauth.integrations.find_by(authenticated=True)
# Combine multiple criteria
integration = client.oauth.integrations.find_by(
name="^github$",
authenticated=True
)# Find by name (supports regex, using anchors for exact match)
integration <- rstudioapi::findOAuthIntegration(name = "^github$")
# Find authenticated integrations
integration <- rstudioapi::findOAuthIntegration(authenticated = TRUE)
# Combine multiple criteria
integration <- rstudioapi::findOAuthIntegration(
name = "^github$",
authenticated = TRUE
)View findOAuthIntegration() documentation or run ?rstudioapi::findOAuthIntegration in your Positron Pro / RStudio IDE R console.
Automatic token refresh
Workbench automatically handles refreshing access tokens for OAuth integrations when the OAuth provider supports it. Token refresh happens transparently when you call get_credentials() (posit-sdk) or getOAuthCredentials() (rstudioapi).
How it works:
- When you request credentials, Workbench checks if the current access token is expired or close to expiring.
- If refresh is needed and the provider supports it, Workbench automatically uses the refresh token to obtain a new access token.
- The new token is returned to you without any additional action required.
- This process is transparent. You always receive a valid access token when available.
What this means for your code:
- You don’t need to implement token refresh logic yourself.
- Simply call
get_credentials()(posit-sdk) orgetOAuthCredentials()(rstudioapi) each time you need a token. - Check the
expiryfield to know when the token will expire. - If automatic refresh fails (e.g., refresh token expired), the Python SDK returns
Noneand the R SDK throws an error. When this happens, you should re-authenticate via the Managed Credentials settings.
Rather than caching tokens in your code, call the credentials function each time you need a token. Workbench’s automatic refresh ensures you get a valid token.
Best practices
Security
- Never log tokens. Avoid printing or logging OAuth tokens in your code. Tokens should only be used for authenticated API requests.
- Review OAuth scopes. Pay attention to the permissions (scopes) requested during the OAuth flow. Ensure they align with what your code actually needs.
Token management
- Rely on automatic refresh. Call
get_credentials()(posit-sdk) orgetOAuthCredentials()(rstudioapi) each time you need a token rather than caching it. Workbench handles refresh automatically. - Handle authentication failures. Implement proper error handling for when credentials are unavailable (Python returns
None, R throws an error), which indicates re-authentication is needed. - Check expiry for long-running operations. For operations that span extended time periods, check the token’s expiry time to ensure it remains valid.
Troubleshooting
OAuth flow doesn’t complete (e.g. errors on provider sign-in or Workbench homepage):
- Ensure you’re accessing Workbench via HTTPS.
- Check that pop-up blockers aren’t preventing the OAuth window from opening.
- If you see “Invalid redirect URI” errors, contact your administrator to verify the OAuth application configuration.
Python get_credentials() returns None or R getOAuthCredentials() throws an error:
- Verify you are authenticated to the integration in the Managed Credentials settings. If not, sign in to the integration. You may need to restart your session after authenticating for the credentials to become available.
- Check that you’re using the correct integration GUID.
- If the integration was working before, sign out and back in through the Managed Credentials settings to refresh the authentication.
API calls to the OAuth provider fail:
- Verify the token hasn’t expired by checking the
expiryfield. - Confirm the OAuth scopes include the permissions required by the API you’re calling. See Viewing integration details to check the scopes configured for your integration.
- Check the OAuth provider’s service status and documentation.
For persistent issues, contact your administrator with the integration name and any error messages.