Python
This page explores how Python can be used together with R and RStudio.
Getting started
RStudio uses the reticulate R package to interface with Python, and so RStudio’s Python integration requires:
An installation of Python (2.7 or newer; 3.5 or newer preferred), and
The reticulate R package (1.20 or newer, as available from CRAN)
Installing python
First, Python needs to be installed on the machine. For Posit Workbench or RStudio Server, admins can follow the instructions at https://docs.posit.co/resources/install-python/
For local installations, Python can be installed in several ways:
(Recommended) Using
reticulate::install_miniconda(), to install a Miniconda distribution of Python using the reticulate package,(Windows) Install Python via the official Python binaries available from https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/,
(macOS) Install Python via the official Python binaries available from https://www.python.org/downloads/mac-osx/,
(Linux) Install Python either from sources, or via the version of Python provided by your operating system’s package manager. See https://docs.python.org/3/using/unix.html for more details. If you are installing Python from sources yourself, prefer installing it into a location like
/opt/python/<version>, so that RStudio and reticulate can more easily discover it.
--enable-shared requirement
reticulate is unable to bind to a version of Python without an accompanying shared library available. If installing Python from sources, it must be configured with --enable-shared:
./configure --enable-shared
make
make installor for pyenv
env PYTHON_CONFIGURE_OPTS="--enable-shared" pyenv install ${PY_VERSION}Installing reticulate
The reticulate package can be installed from CRAN, with:
install.packages("reticulate")The dev version of reticulate can be installed from GitHub, with:
# If needed, install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("rstudio/reticulate")If you are installing reticulate from sources or GitHub, you will need the requisite build tools available - see https://r-pkgs.org/Setup.html#setup-tools for more details.
Using Python
The reticulate package makes it possible to load and use Python within the currently running R session. After reticulate has been installed, Python scripts (with the extension .py) can be opened, and the code within executed interactively, similarly to R.
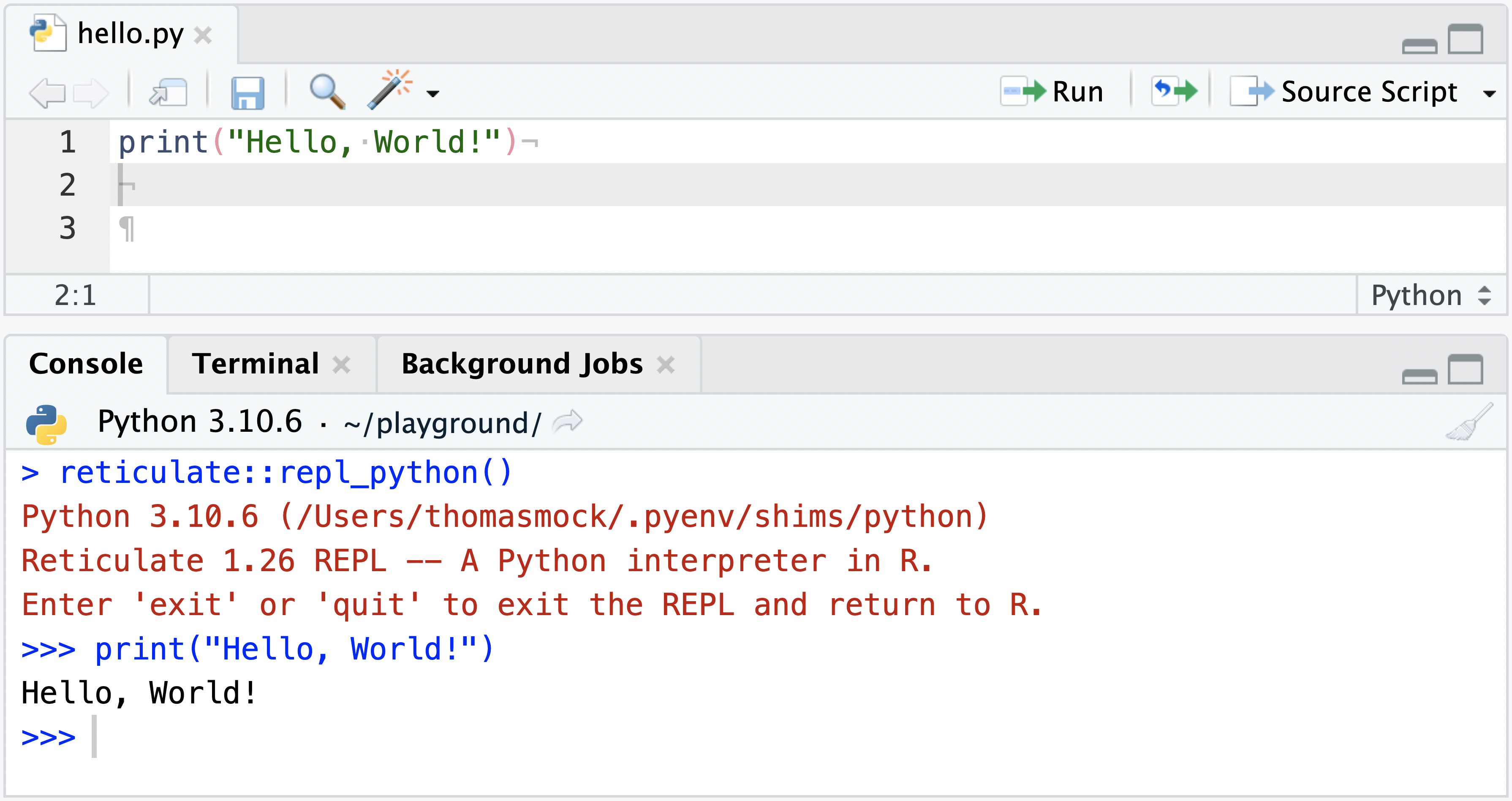
RStudio uses the reticulate Python REPL to execute code, and automatically switches between R and Python as appropriate for the script being executed.
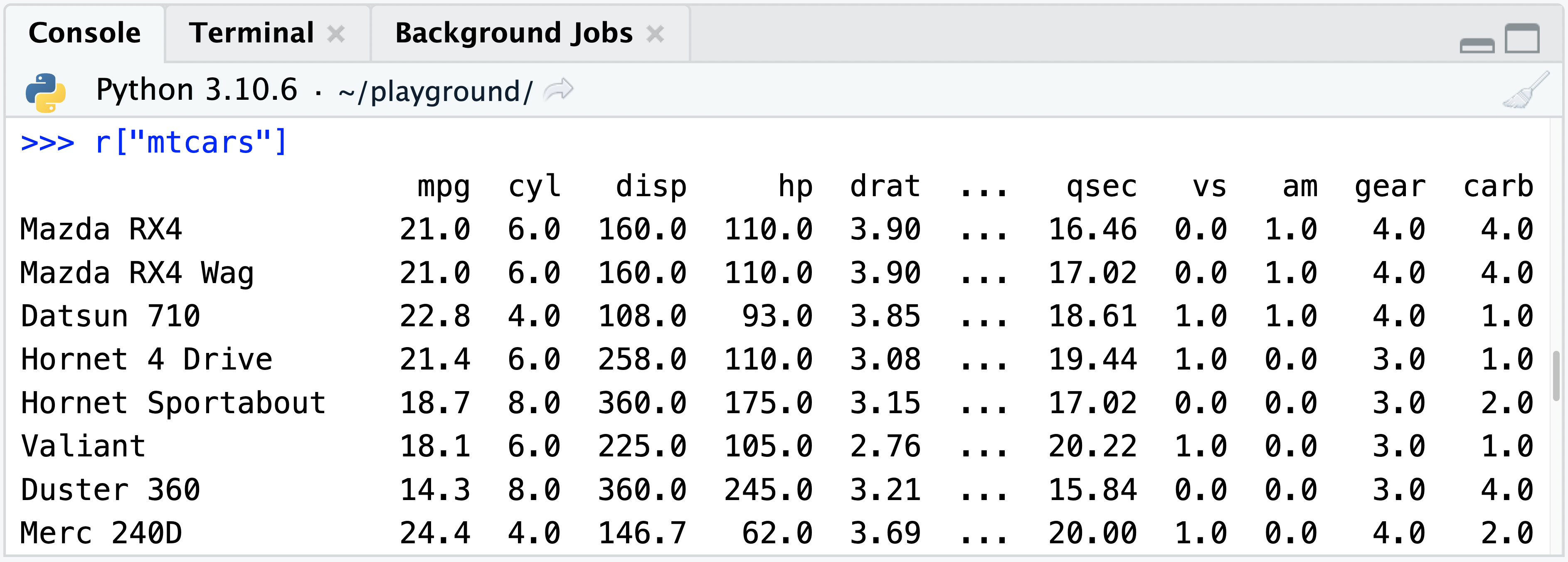
When the reticulate REPL is active, objects in the R session can be accessed via the r helper object. For example, r["mtcars"] can be used to access the mtcars dataset from R, and convert that to a pandas DataFrame (if available), or a Python dictionary if not.
Selecting a default version of Python
It is possible to configure a default version of Python to be used with RStudio via Tools > Global Options > Python:
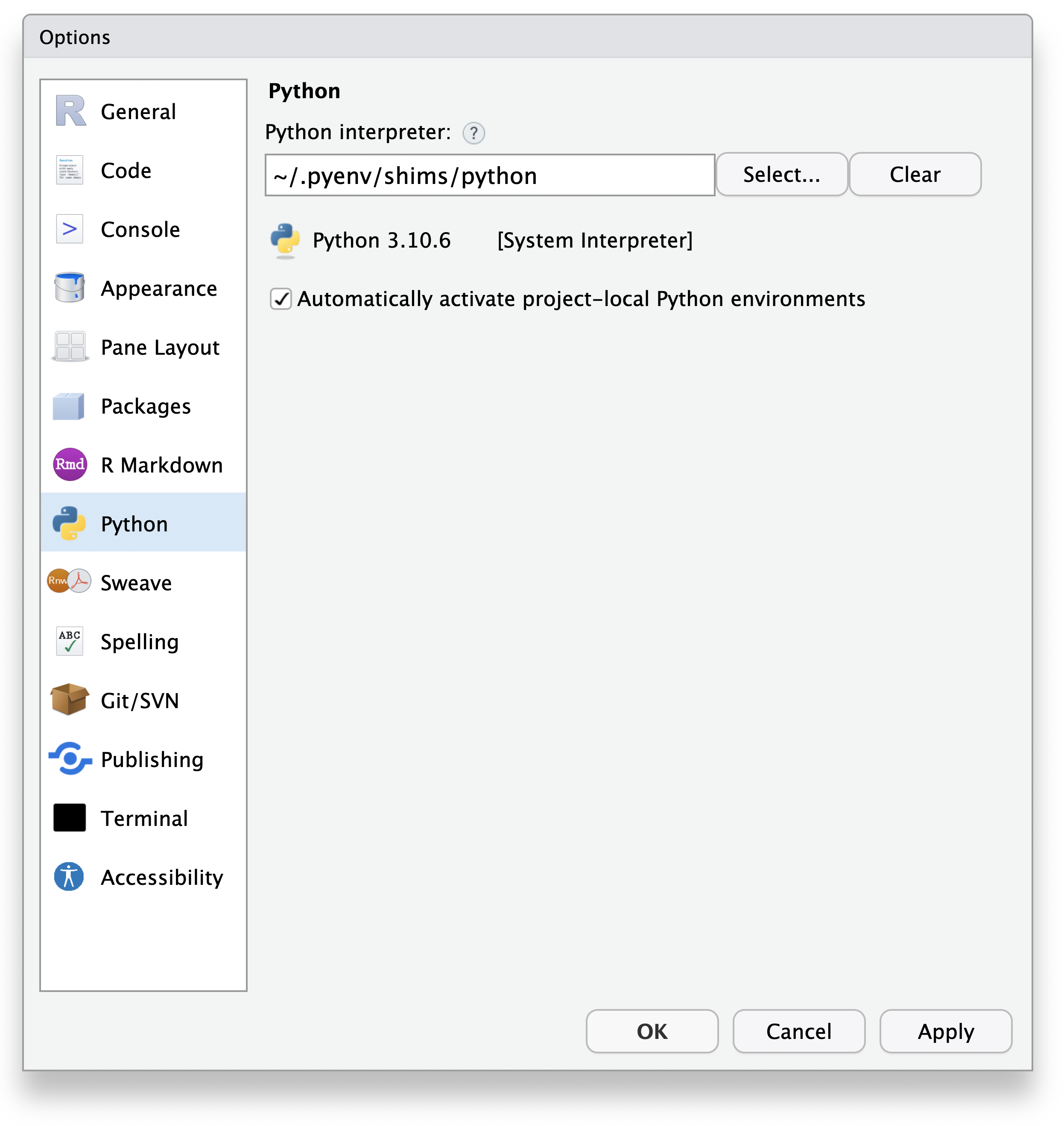
The “Python interpreter:” text box shows the default Python interpreter to be used (if any). If you already know the location of the Python interpreter you wish to use, you can type the location of the interpreter into that text box.
Otherwise, Python interpreters can be discovered on the system by clicking the Select button:
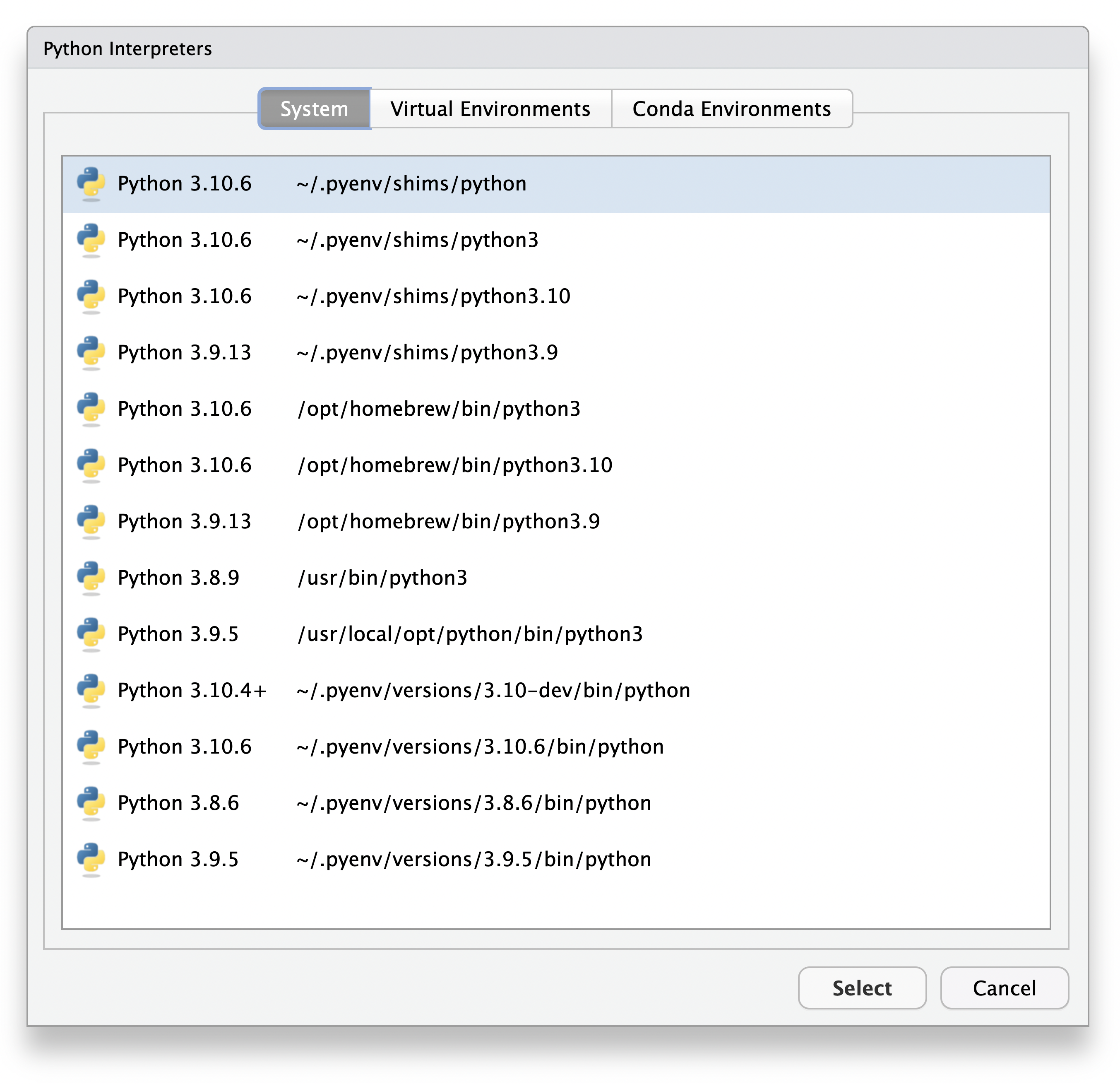
RStudio will search for Python interpreters via a few different methods:
On the PATH;
For virtual environments, located within the
~/.virtualenvsfolder;For Conda environments, as reported by
conda --list,For pyenv Python installations located in
~/.pyenv,For Python installations located in
/opt/python.
The RETICULATE_PYTHON environment variable can also be used to configure the default version of Python to be used by reticulate. If set, that environment variable will take precedence over any value configured via RStudio options.
Custom Python locations
If Python is installed into a custom location, set the following R option to make it visible to RStudio:
options(rstudio.python.installationPath = "/path/to/python")This can be set within an appropriate R startup file; for example, the R installation’s etc/Rprofile.site.
Environment pane
When the reticulate Python REPL is active, the Environment pane will update to show any available Python objects. For example:
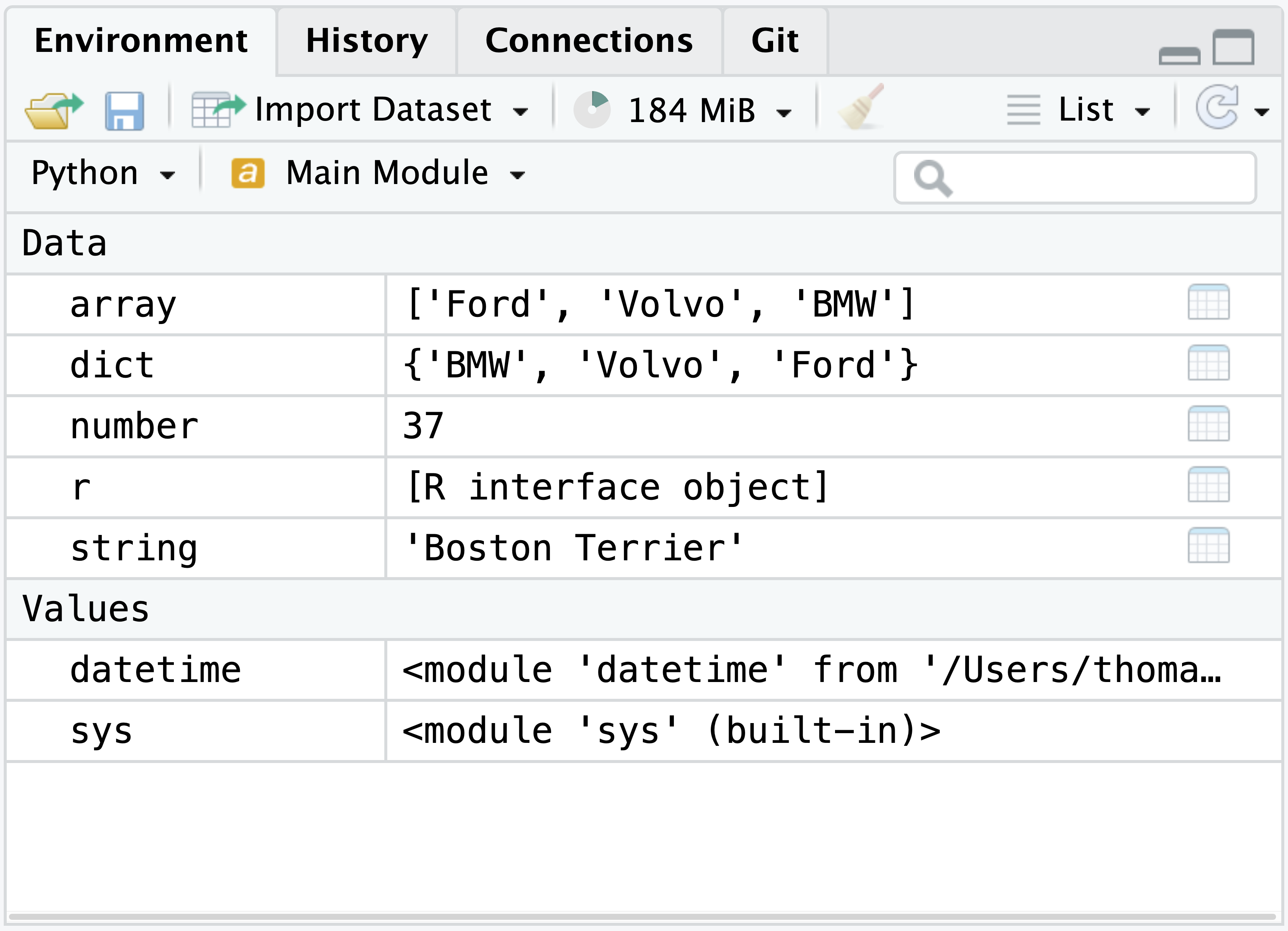
The Environment pane will automatically update to show objects as they are added and removed.
Mutated objects may not update in the Environment pane until the Environment pane is explicitly refreshed by pressing the Refresh button in the top right corner of the Environment pane.
Learning more
For more detailed documentation around how Python, R, and reticulate can be used together, please consult the reticulate documentation online at https://rstudio.github.io/reticulate/.