Managing R
R startup
Upon startup, R and RStudio look for a few different files used to control the behavior of the R session (e.g., settings options or environment variables).
In the context of Posit Team, these settings are often used to direct Posit Workbench to search for packages in a Posit Package Manager repository.
This section is a practical guide on how to set particular options on R startup. For more information on:
- How to manage R package environments, refer to the Posit Solutions guide on Reproducible Environments
- A deeper treatment of R process startup, refer to What They Forgot to Teach You About R
Here is a summary table of how to control R options and environment variables on startup:
| File | Who Controls | Level | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
.Renviron |
User or Admin | User or Project | Set environment variables only. |
.Rprofile |
User or Admin | User or Project | None, sourced as R code. |
Rprofile.site |
Admin | Version of R | None, sourced as R code. |
Renviron.site |
Admin | Version of R | Set environment variables only. |
rsession.conf |
Admin | Server | Only RStudio settings, only single repository. |
repos.conf |
Admin | Server | Only for setting repositories. |
.Renviron
The .Renviron file is:
A user-controllable file used to create environment variables.
Written in a key-value format. Environment variables are created in the format:
Key1=value1 Key2=value2 ...additional key=value pairs- In this example,
Sys.getenv("Key1")will return"value1"in an R session.
- In this example,
Located at either the user or project level. If there is a project-level
.Renvironfile, the user-level file will not be sourced.Most useful for defining sensitive information like API keys (e.g., GitHub, Twitter, or Posit Connect), as well as R-specific environment variables like the history size (
R_HISTSIZE=100000) and default library locationsR_LIBS_USER.
The usethis package includes a helper function for editing .Renviron files from an R session with usethis::edit_r_environ(). You can specify whether you want to edit the user or project level .Renviron.
.Rprofile
The .Rprofile file:
- Contains R code that is run when R starts up, after the
.Renvironfile is sourced. - Is user-controllable, and sets options and environment variables.
- Can be located either at the user or project level. User-level
.Rprofilefiles live in the base of the user’s home directory. Project-level.Rprofilefiles live in the base of the project directory.- If there is a project-level
.Rprofilefile, the user-level file will not be sourced. In this situtaion, if you want the user-level file to be sourced, explicitly source it at the top of your project-level.Rprofilewithsource("~/.Rprofile").
- If there is a project-level
- Are sourced as regular R code, so setting environment variables must be done inside a
Sys.setenv(key = "value")call.
A simple example of a .Rprofile is:
options(repos = c(CRAN = "https://packagemanager.posit.co/all/latest"))
if (interactive()) {
options(width = 120)
}The usethis package includes a helper function for editing .Rprofile files from an R session with usethis::edit_r_profile(). You can specify whether you want to edit the user or project level .Rprofile.
Rprofile.site and Renviron.site
Both .Rprofile and .Renviron files have equivalents that apply server wide: Rprofile.site andRenviron.site (no leading dot). These files are:
- Managed by admins on Posit Workbench or RStudio Server.
- Specific to a particular version of R.
- Most commonly used to manage settings related to package repository access.
- For example, administrators generally use the
Rprofile.sitefile to implement the shared-baseline package management strategy.
- For example, administrators generally use the
- Able to be overriden by users in their individual
.Rprofileor.Renvironfiles. - Set for each version of R, and should be located in
R_HOME/etc/.R_HOMEcan be found by running the commandR.home(component = "home")in a session of that version of R.- For example: if
R_HOMEis/opt/R/4.2.0/lib/R, theRprofile.sitefor R 4.2.0 would go in/opt/R/4.2.0/lib/R/etc/Rprofile.site.
- For example: if
rsession.conf and repos.conf
The rsession.conf and repos.conf files allow Posit Workbench and RStudio Server administrators to configure particular server-wide R package repositories.
Only one repository can be configured in rsession.conf. If multiple repositories are needed, administrators should use repos.conf. Details on configuring Posit Workbench and RStudio Server with these files are in the Package Installation section of the Posit Workbench Admin Guide guide.
Managing R versions
RStudio requires R version 3.6.0 or higher. Since multiple R versions can be installed side-by-side on a system, RStudio needs to select which version of R to run against.
Using rig to manage R versions
The simplest way to manage your installed R versions is to use the rig R Installation Manager. It works on macOS, Windows, and Linux operating systems.
For more information and to download it, visit the rig GitHub repository and review the README.
Once you have installed rig, you can use the rig rstudio command to start RStudio with a specified R version. For example, to start RStudio with R version 4.3.0, run:
rig rstudio 4.3.0Managing R versions manually on Windows
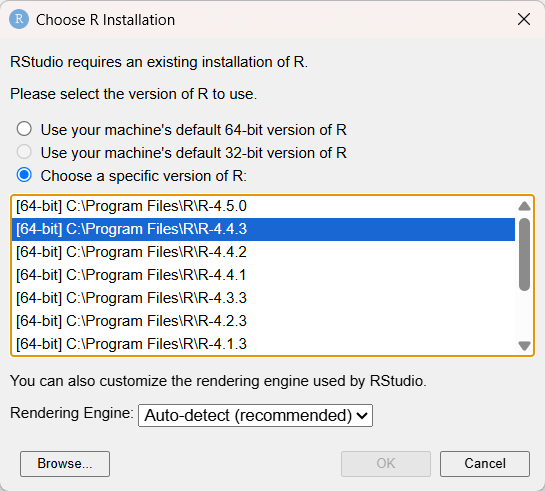
You can override which R version RStudio uses on a Windows machine by navigating to Tools > Global Options > General > Basic > R Sessions. Select Change next to the R Version field.
A Choose R Installation dialog displays that allows you to select the version of R to use. This dialog box, pictured below, also appears if you hold down the Ctrl key at RStudio startup.