Executing code
RStudio supports the direct execution of code from within the source editor (the executed commands are inserted into the console where the output also appears).
Source files
Source code files such as .R or .py can be executed in several different ways.
Executing a single line
To execute the line of source code where the cursor currently resides press the Ctrl+Enter keys (or use the Run toolbar button):
After executing the line of code, RStudio automatically advances the cursor to the next line. This enables single-stepping through a sequence of lines.
Executing multiple lines
There are three ways to execute multiple lines from within the editor:
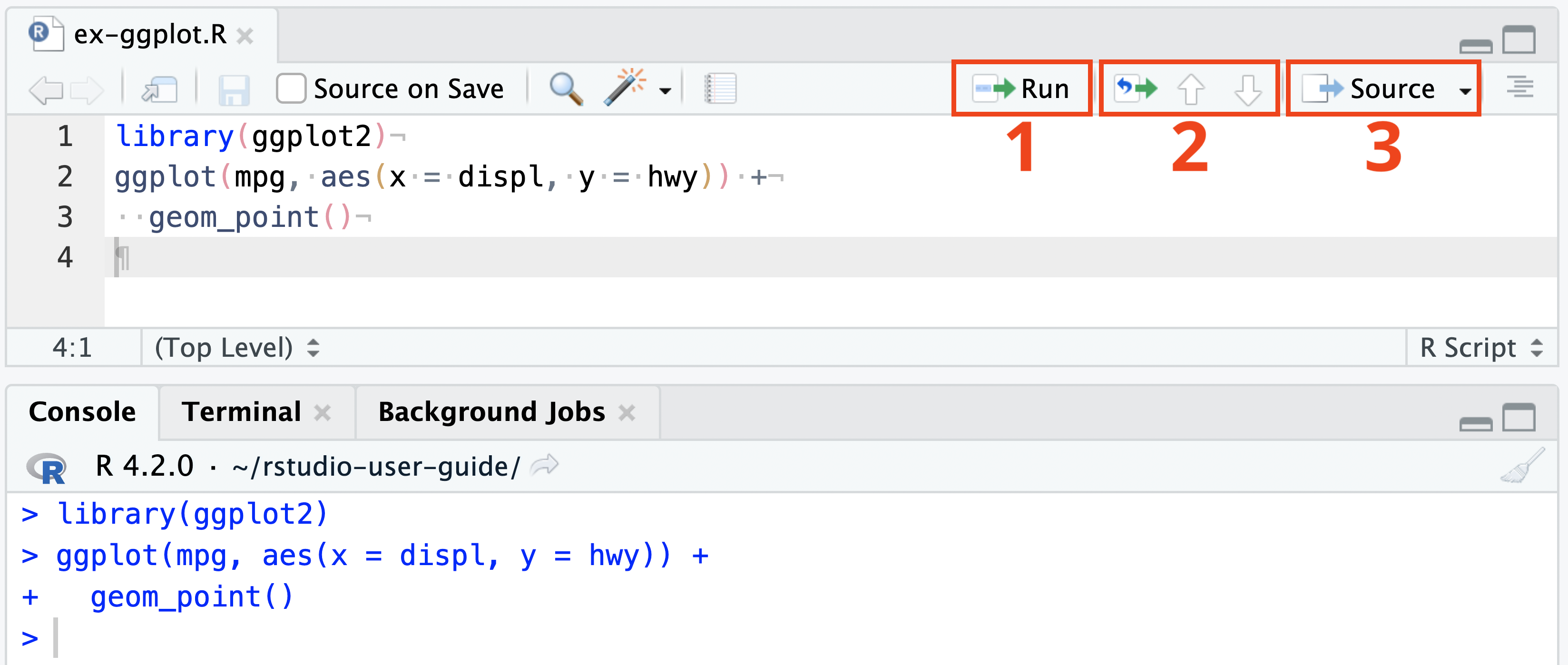
Select the lines and press the Ctrl+Enter keys (or use the Run toolbar button); or
After executing a selection of code, use the Re-Run Previous Region command (or its associated toolbar button) to run the same selection again. Note that changes to the selection including additional, removal, and modification of lines will be reflected in this subsequent run of the selection.
To run the entire document press the Ctrl+Shift+Enter keys (or use the Source toolbar button).
The difference between running lines from a selection and invoking Source is that when running a selection all lines are inserted directly into the console whereas for Source the file is saved to a temporary location and then sourced into the console from there (thereby creating less clutter in the console).
Source on save
When editing re-usable functions (as opposed to freestanding lines of R) you may wish to set the Source on Save option for the document (available on the toolbar next to the Save icon). Enabling this option will cause the file to automatically be sourced into the global environment every time it is saved.
Setting Source on Save ensures that the copy of a function within the global environment is always in sync with its source, and also provides a good way to arrange for frequent syntax checking as you develop a function.
Computational documents
Code within computational documents such as Quarto or R Markdown is written inside “code chunks” as written below:
```{r}
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point()
```Similar to source code files, code can be executed via RStudio “Run” commands or keyboard shortcuts Ctrl + Enter. However, each chunk also has a green “Run” button to execute that specific chunk.

Executing a single line
To execute the line of source code where the cursor currently resides press the Ctrl+Enter keys (or use the Run toolbar button):
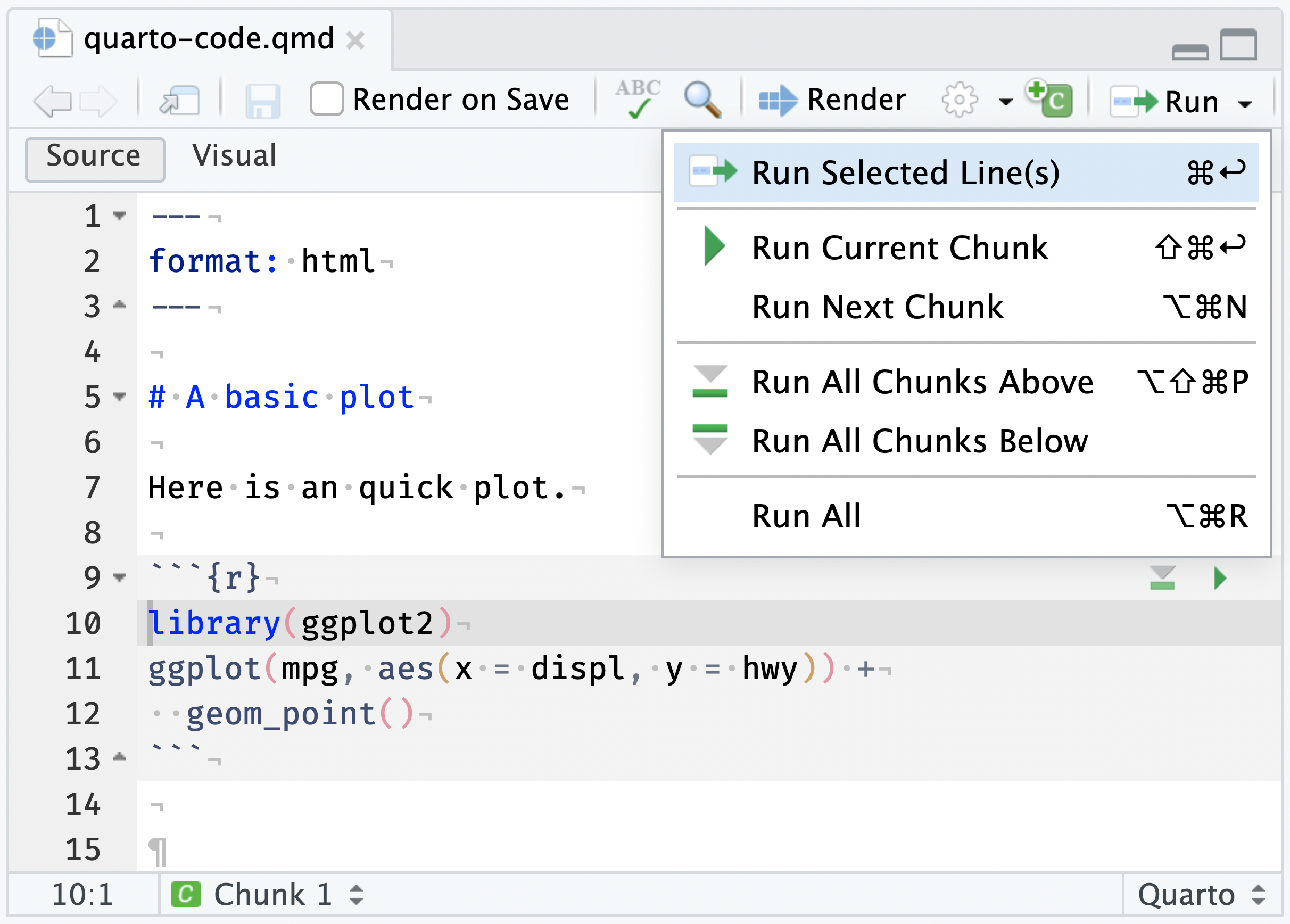
After executing the line of code, RStudio automatically advances the cursor to the next line. This enables you to single-step through a sequence of lines.
Executing multiple lines
There are four ways to execute multiple lines from within the editor:
Select the lines and press the Ctrl+Enter key (or use the Run toolbar button); or
To run the entire document press the Ctrl+Alt+R keys (or use the Run All toolbar button).
To run the entire document and convert it to the final output, use the Knit or Render button.
To run an entire cell, press the “Run Current Chunk” button on the code chunk, or in the Run toolbar via “Run Current Chunk”, or with the Ctrl+Shift+Enter shortcut
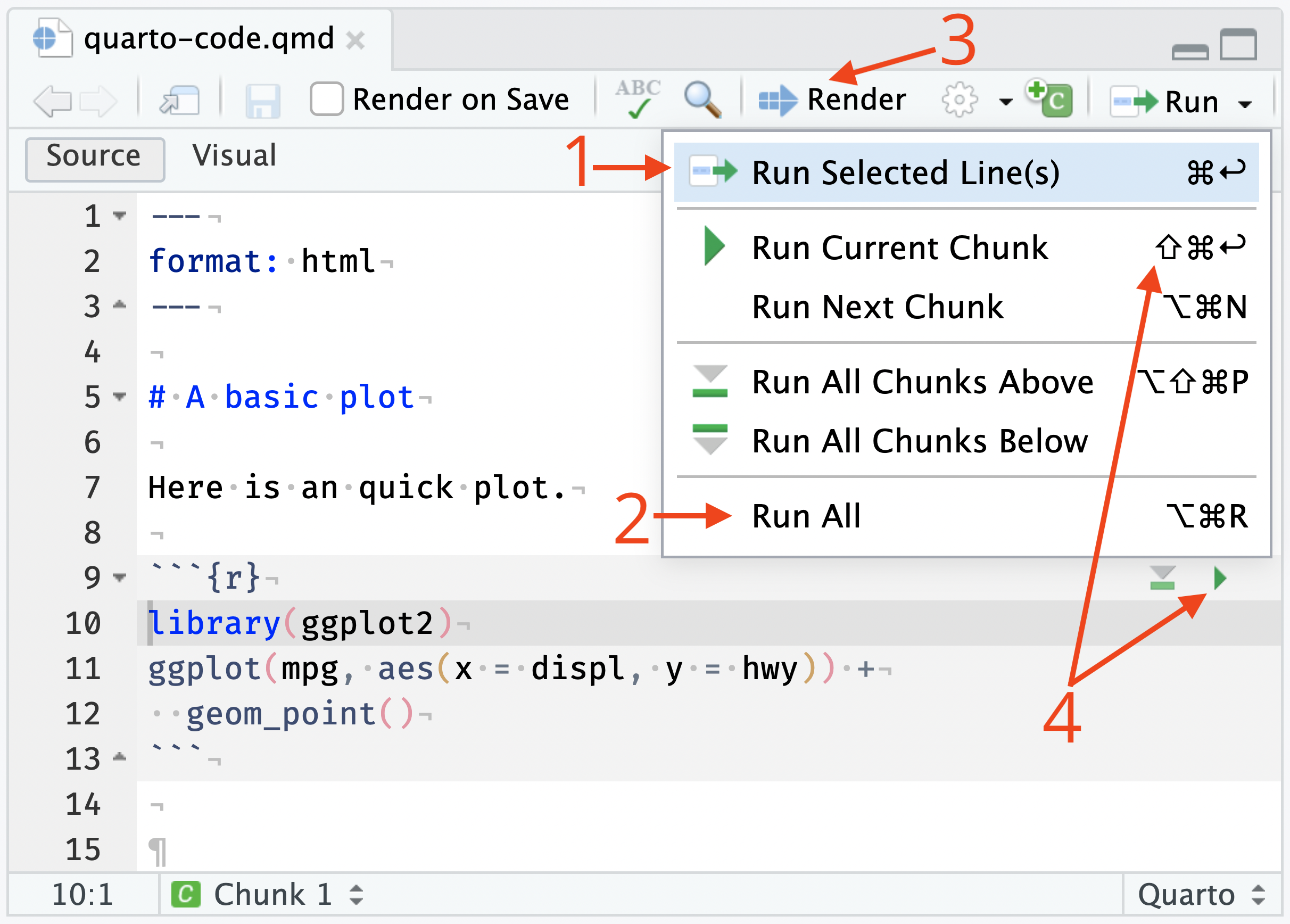
The difference between running the entire document and invoking Knit/Render is that when running a selection all lines are inserted directly into the console whereas for Knit/Render the code is executed in a fresh separate R session and the file is rendered to its output format.
Render on Save
When editing Quarto documents (as opposed to editing freestanding lines of code in .R files) you may wish to set the Render on Save option for the document (available on the toolbar next to the Save icon). Enabling this option will cause the file to automatically be rendered and the display updated in the Viewer pane every time you save.
Setting Render on Save ensures that the displayed output is in sync with its source, and also provides a good way to arrange for frequent visual checking as you author a computational document.