python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate Deploy a LLM-powered Shiny for Python App with Secrets
This tutorial creates a Shiny for Python application that leverages an OpenAI API key and deploys it to Posit Connect Cloud. Code for the application is available on GitHub.
1. Create a new repo
Sign in to GitHub and create a new, public repository.
2. Start a new project
Start a new project in your preferred development environment. In VS Code, for example, select New Window from the File Menu and then click Start >> Clone Git Repository. Paste the link to your new repository.
3. Create a virtual environment
In the terminal, create a virtual environment named venv and activate it. This will isolate the specific packages we need for the application.
4. Install required packages
shiny==1.1.0
pandas==2.2.3
requests==2.32.3This example makes use of the above Python packages and they need to be installed in your virtual environment.
Create a requirements.txt file, adding each package on a new line. This file helps install everything the application needs to run locally and will ultimately tell Connect Cloud what it needs to deploy the application.
Once you have saved requirements.txt, run the following command in the terminal to install all the packages into your virtual environment.
pip install -r requirements.txt5. Build the application
Create a new file named app.py. Copy and paste the following code into the file.
import os
import pandas as pd
import requests
import io
import re
from shiny import App, reactive, render, ui
from htmltools import css
# Internal API key (replace with your actual API key)
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
app_ui = ui.page_fluid(
ui.tags.br(),
ui.panel_title("AI Dataset Generator"),
ui.layout_sidebar(
ui.sidebar(
ui.input_text("description", "Describe the dataset you want",
placeholder="e.g., health data for a family of 4"),
ui.input_action_button("generate", "Generate Dataset"),
ui.output_ui("download_button"), # New output for dynamic button
ui.tags.br(), ui.tags.br(),
ui.output_ui("summary"),
ui.tags.hr(),
ui.tags.small("Note: Generated data may not be accurate or suitable for real-world use. The maximum number of records is limited to 25."),
open="open",
width=350
),
ui.navset_tab(
ui.nav_panel("Data Table",
ui.tags.br(),
ui.output_data_frame("dataset_output")
)
)
)
)
def server(input, output, session):
dataset_rv = reactive.value(None)
summary_text = reactive.value("")
show_download_button = reactive.value(False) # New reactive value
def preprocess_csv(csv_string):
# Extract only the CSV part
csv_pattern = r"(?s)(.+?\n(?:[^,\n]+(?:,[^,\n]+)*\n){2,})"
csv_match = re.search(csv_pattern, csv_string)
if not csv_match:
raise ValueError("No valid CSV data found in the response")
csv_data = csv_match.group(1)
try:
df = pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(csv_data))
except pd.errors.EmptyDataError:
raise ValueError("The CSV data is empty or malformed")
except pd.errors.ParserError:
raise ValueError("Unable to parse the CSV data")
# Clean column names
df.columns = df.columns.str.lower().str.replace(r'[^\w\s]', '', regex=True).str.replace(' ', '_')
# Convert numeric columns
for col in df.columns:
try:
df[col] = pd.to_numeric(df[col])
except ValueError:
pass
return df
def generate_summary(df):
prompt = f"""Summarize the following dataset:
Dimensions: {df.shape[0]} rows and {df.shape[1]} columns
Variables:
{', '.join(df.columns)}
Please provide a brief summary of the dataset dimensions and variable definitions. Keep it concise, about 3-4 sentences."""
response = requests.post(
"https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}"},
json={
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant that summarizes datasets."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
content = response.json()
summary = content['choices'][0]['message']['content']
return summary
else:
return "Error generating summary. Please try again later."
@reactive.Effect
@reactive.event(input.generate)
def _():
description = input.description()
if not description:
return
with ui.Progress(min=1, max=3) as p:
p.set(1, message="Generating dataset...")
prompt = f"Generate a fake dataset with at least two variables as a CSV string based on this description: {description} Include a header row. Limit to 25 rows of data. Ensure all rows have the same number of columns. Do not include any additional text or explanations."
response = requests.post(
"https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {OPENAI_API_KEY}"},
json={
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant that generates fake datasets."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
content = response.json()
csv_string = content['choices'][0]['message']['content']
try:
p.set(2, message="Processing data...")
df = preprocess_csv(csv_string)
dataset_rv.set(df)
p.set(3, message="Generating summary...")
summary = generate_summary(df)
summary_text.set(summary)
show_download_button.set(True) # Show the download button
except Exception as e:
ui.notification_show(f"Error processing data: {str(e)}", type="error")
else:
ui.notification_show("Error generating dataset. Please try again later.", type="error")
@output
@render.data_frame
def dataset_output():
df = dataset_rv()
if df is not None:
return df
return None
@output
@render.download(filename="generated_dataset.csv")
def download():
df = dataset_rv()
if df is not None:
return io.BytesIO(df.to_csv(index=False).encode())
return io.BytesIO(b"No data available") # Return an empty file if no data
@output
@render.ui
def download_button():
if show_download_button():
return ui.download_button("download", "Download CSV")
return None
@output
@render.ui
def summary():
if summary_text():
return ui.div(
ui.h4("Dataset Summary"),
ui.p(summary_text()),
style=css(
background_color="#f0f0f0",
padding="10px",
border_radius="5px"
)
)
app = App(app_ui, server)The application relies on an API key from OpenAI, which is called at the top of app.py with os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY").
Using a dedicated environment variable file helps keep your secret key out of the application source code. This is important because we will ultimately push it to a public GitHub repository.
Create a file named .env.
touch .envOpen the new file and add your API key for this project. Learn more about creating the API key here.
OPENAI_API_KEY='your-api-key-here'6. Preview the application
From the terminal, run the following command.
shiny run app.py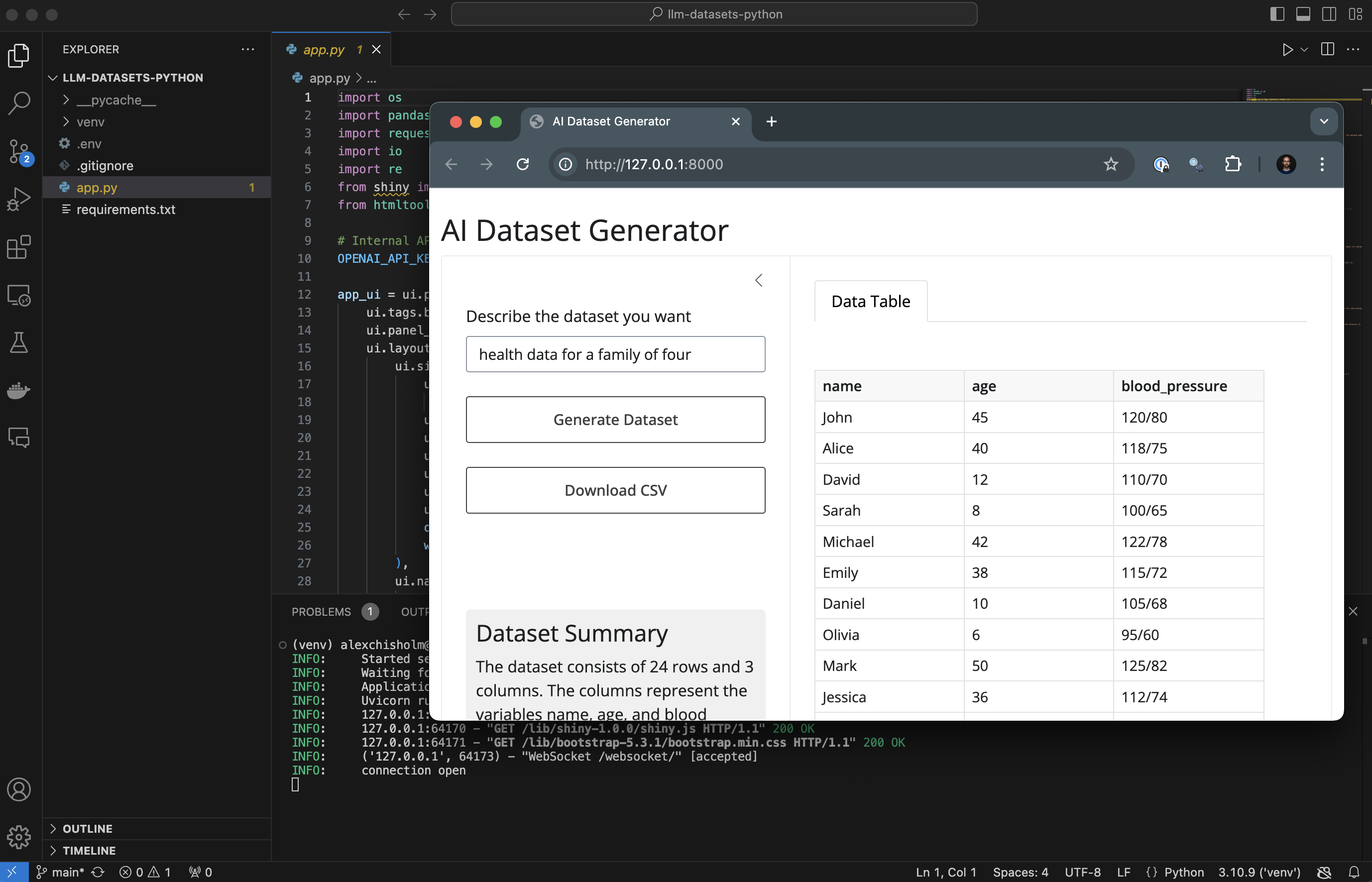
Now that everything looks good and we’ve created a file to help reproduce your local environment, it is time to get the code on GitHub.
7. Push to GitHub
Before syncing your project with the new repository, create a .gitignore file to indicate which files should not be included in that transfer.
touch .gitignoreAdd the virtual environment folder and the envrionment variables file to the file.
venv/
.envYou are now ready to push your work to GitHub.
git init .
git commit -m "project v1.0"
git push -u origin mainFinally, refresh your GitHub repository page. You should see everything that was in your local directory with the exception of what was added to the .gitignore file.
8. Deploy to Posit Connect Cloud
Follow the steps below to deploy your project to Connect Cloud.
Sign in to Connect Cloud.
Click the Publish icon button on the top of your Home page
Select Shiny
Select the public repository that you created in this tutorial
Confirm the branch
Select app.py as the primary file
Click Advanced settings
Click “Add variable” under “Configure variables”
In the Name field, add
OPENAI_API_KEYIn the Value field, add your secret OpenAI API key
Click Publish
Publishing will display status updates during the deployment process. You will also find build logs streaming on the lower part of the screen.
Congratulations! You successfully deployed to Connect Cloud and are now able to share the link with others.
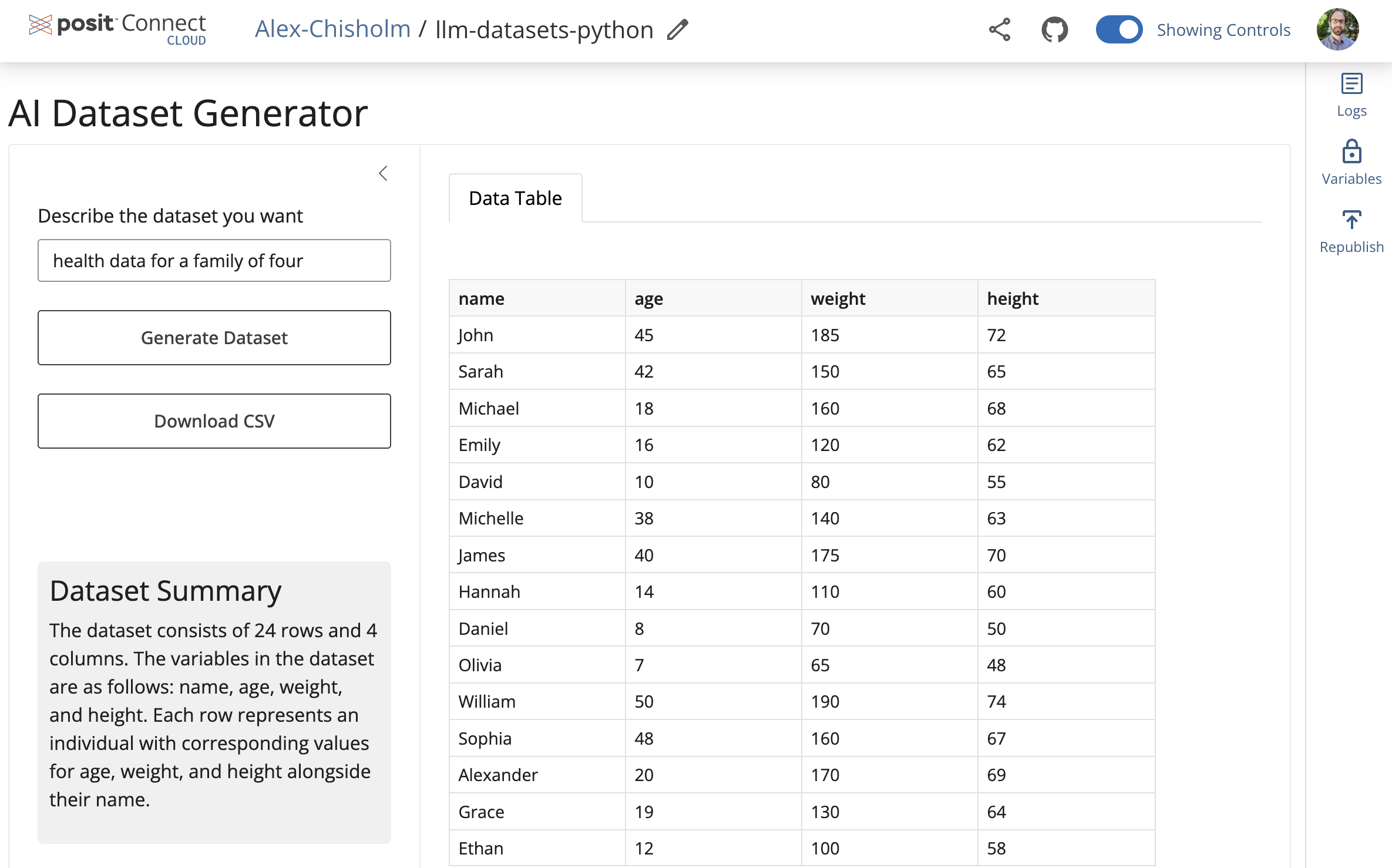
9. Republish the application
If you update the code to your application or the underlying data source, commit and push the changes to your GitHub repository.
Once the repository has the updated code, you can republish the application on Connect Cloud by going to your Content List and clicking the republish icon.