Pane Layout
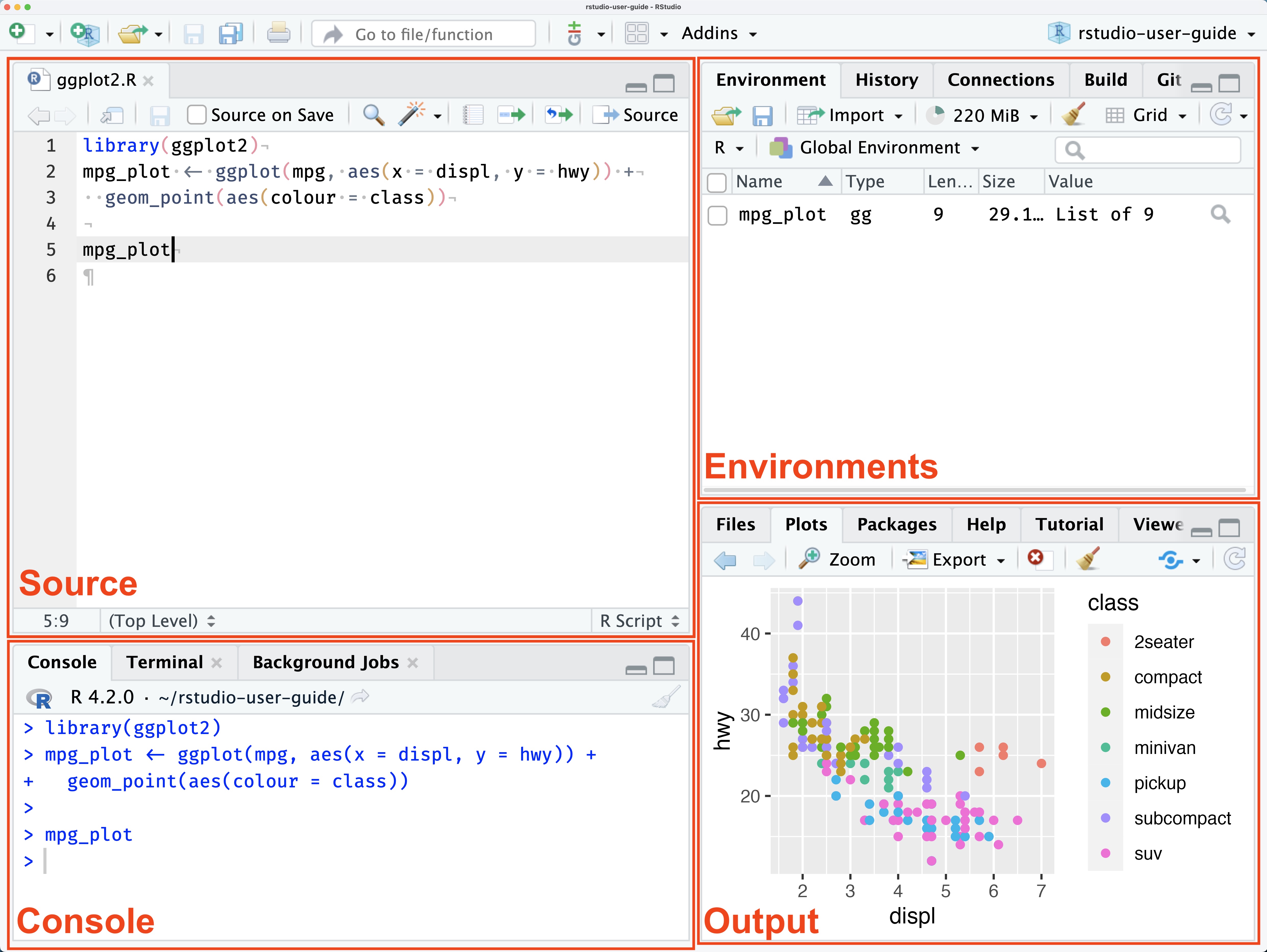
The RStudio user interface has 4 primary panes:
- Source pane
- Console pane
- Environment pane, containing the Environment, History, Connections, Build, VCS , and Tutorial tabs
- Output pane, containing the Files, Plots, Packages, Help, Viewer, and Presentation tabs
Each pane can be minimized or maximized within the column by clicking the minimize/maximize buttons ![]() .
.
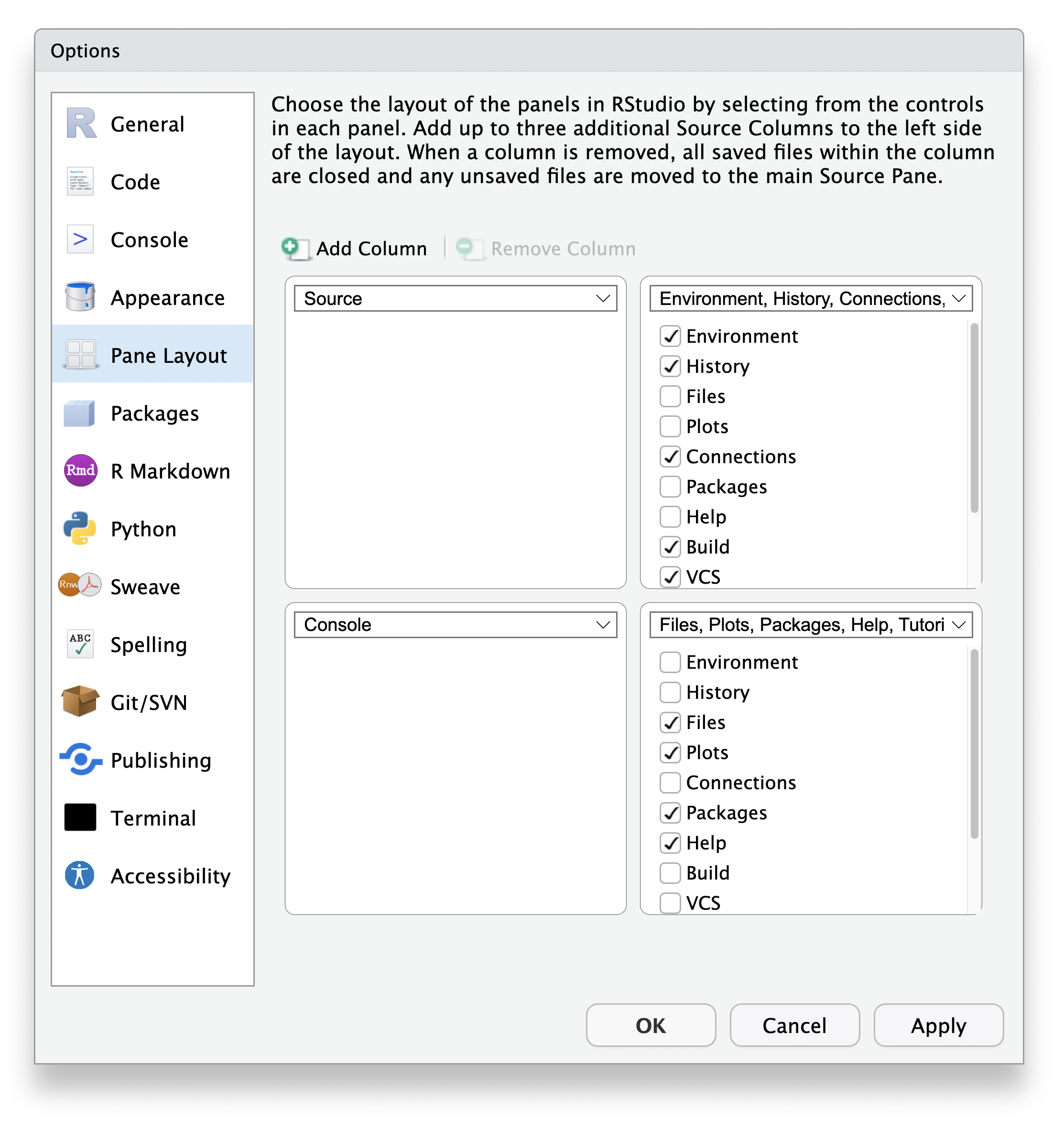
The documentation below provides information based on the default layout/options of each pane. The specific components within each pane and overall arrangement of panes can be modified by opening the Tools > Global Options > pane Layout.
Additional source “columns” can be added to the left of the four primary panes. To add additional source columns, from the RStudio menu: Global Options > Pane Layout > Add Source Column, which provides the ability to work on two (or more) source files at a time within the Source Pane.
Source
The source pane allows users to view and edit various code-related files, such as .R, .rmd, .qmd, .py, .css, or general text files such as .txt or .md. By default it is the top-left panel and can be launched by opening any editable file in RStudio. Each additional file that is opened will be added as a new tab within the Source pane.
Additional source “columns” can be added to the left of the four primary panes. To add additional source columns, from the RStudio menu: Global Options > pane Layout > Add Source Column, which provides the ability to work on two (or more) source files at a time within the Source pane.
Individual source files can also be opened in their own window, rather than only within the Source pane. Source windows allow you to edit files outside the main RStudio window. This is useful for splitting your work among multiple monitors, or devoting more space to your editor.
Creating Source Windows
There are two ways to open a new source window:
Pop out an editor: click the Show in New Window button in any source editor tab.
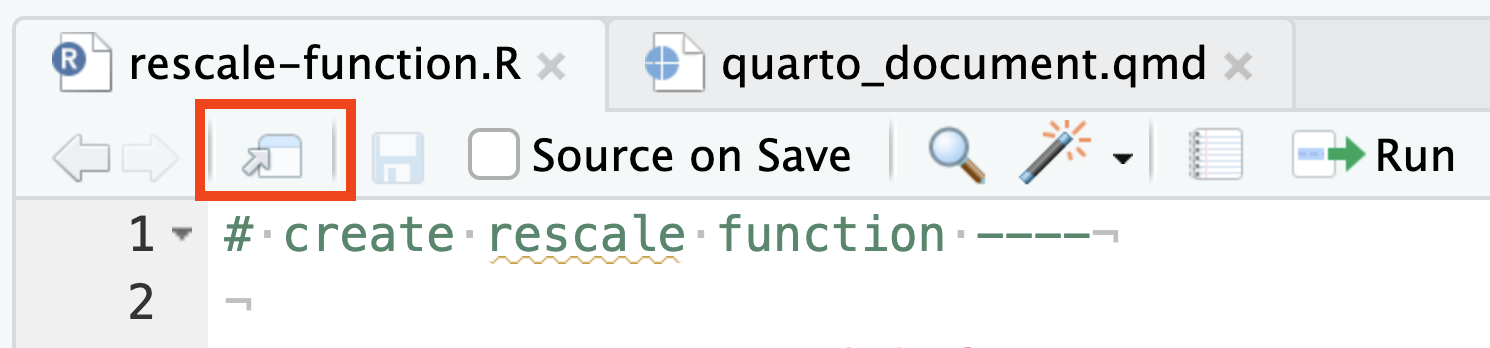
Tear off a pane: drag a tab out of the main Source pane and onto the desktop; a new source window will be created where you dropped the tab.
You can have as many source windows open as you like.
Managing Source Windows
Each source window has its own set of tabs; these tabs are independent of the tabs in RStudio’s main source pane.
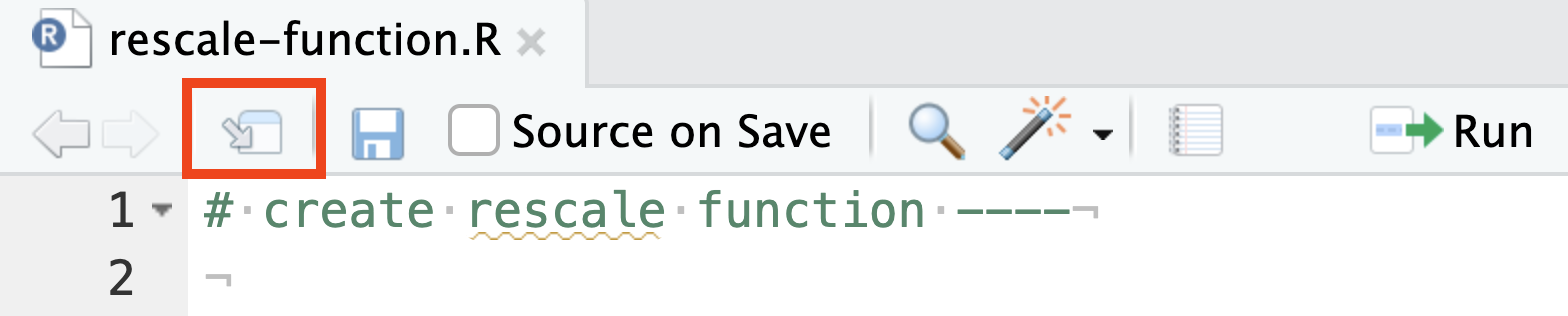
To return a document to the main window, click the Return to Main Window button on the editor toolbar.
.R
R source files .R have a Undo/Redo arrows, a Show in New Window button to tear out that pane into it’s own window, a Save button along with a “Source on Save” button that will source the entire script each time it is saved. There is Find/Replace button and then code-tools button. A .R file can be compiled into a report.
The right side of the menu bar has a run button to run the selected line, a Re-Run button to rerun the previous code, a source drop-down button for sourcing the file silently, with echo, or as a Background Job. The last icon opens a document outline which will display section labels in the code. Section labels are written as special comments:
# section name ----Subsections can be indicated by increasing the number of #:
# Heading 1 ----
## Subheading ----
### Smaller subheading ----
# Section 2 ----
## Subheading 2 ----.qmd
Quarto documents (.qmd) have a toggle-able Source or Visual mode for displaying real time view of the formatted markdown, along with a Save button, a Render on Save, Spellcheck, search, Render button, a gear for selecting whether to have inline output or output to the R console or Plot pane.
On the right side of the menu bar there is a section for adding specific language code chunks, a dropdown for running various methods of the code, and a blue publish button for publishing to Posit Connect, Shinyapps.io, Quarto Pubs or RPubs.
Console
By default the console pane is the bottom left pane. The console pane provides an area to interactively execute code. By default it is tied to R, but through the use of the reticulate package, it can also provide a Python console.
The Console pane also includes an integrated Terminal tab for executing system commands, adding or removing additional integrated terminals, as well as general controls of the current selected terminal.
The Background Jobs tab provides the ability to send long running R scripts to local and remote background jobs. This functionality can dramatically improve the productivity of data scientists and analysts using R since they can continue working in RStudio while jobs are running in the background.
Ctrl+1 — Move focus to the Source pane Ctrl+2 — Move focus to the Console Ctrl+L — Clear the Console Esc — Interrupt R
Environment pane
By default, the Environment pane is located in the top-right and includes the Environment, History, Connections, Build, and Version Control System (VCS) tabs.
Environment
The environment tab displays currently saved R and Python objects. For example, the following code would add avg_mpg to the environments pane for the duration of the current session.
avg_mpg <- mean(mtcars$mpg)The R icon can be toggled between R or Python environment objects.
The environment menu bar provides loading or saving of R Workspaces, interactive import of datasets from text files, Excel, or SPSS/SAS/Stata. It also displays the memory currently used by the active R session, and a broom icon to remove all of the current environment objects.
History
The history tab displays the commands that were executed in the current session along with search. There are buttons for loading/saving the command history to a file, as well as sending the selected command into the console or inserting it into the current working document. There is a delete button for deleting the selected history or the broom button for removing all history of the current session.
Connections
The connections tab displays connections to local or remote databases or pins. Additional possible connections can be added by installing database drivers or specific R packages. You can interactively click on available connections and it will provide generic R code to register an active connection with that data source. Once the connection is created, you can then explore available tables or pins in that connection.
There is also a Connect button for creating a connection in the R console, script, or a notebook, as well as copying the relevant code to the clipboard if available.
Build
The Build tab is available in specific R projects that interact with it such as R packages or Quarto/R Markdown websites/books
Based on the type of R Project, the build pane will provide options for building the R Package or rendering the website.
VCS (Version Control System)
The VCS tab will change based on the version control system you have enabled for that session. For example, using Git will change the tab name to Git and provide commands for:
Viewing diffs
Committing selected files
Performing Pull or Push commands
Viewing the version control history
Adding selected files to the .gitignore
Creating or selecting a specific branch
Output pane
By default, the Output pane is the bottom-right pane and displays various outputs such as plots, HTML content, or on-disk files. It contains the Files, Plots, R Packages, Help, Tutorial, Viewer, and Presentation tabs.
Files
This tab provides interactive exploration of the current R Project along with the entire directory. There are menu bar options for adding new folders, new blank files, deletion/renaming of files, as well as a gear pane for additional functions.
Plots pane
This tab will display static images generated by code until the session is restarted. There are backwards and forwards arrows for navigating between older and newer plots that have been displayed, a Zoom feature, an export button for saving displayed outputs, a delete button for removing the currently displayed image, and a broom icon which will clear ALL temporary plots from this tab
Packages
The package tab allows for viewing currently installed R packages, and has a search bar for searching the current library of packages. There is an install and update button for installation of new packages or updating existing selected packages.
Help
The help tab is used to display package documentation and vignettes. There are arrows for navigating backwards and forwards as additional help pages are viewed. The home icon will return to the general help page, with links to Resources, Manuals, References, and Posit Support.
To get help on a specific R function use the ?functionName or help(functionName) syntax, for example the following code when executed would open the help page for the paste0() function:
?paste0()
# or
help(paste0)Additionally, sections of code can be highlighted and executed in the R console with the Ctrl+Enter shortcut (Cmd+Enter on Mac).
Tutorial
The tutorial tab is used to load interactive learnr tutorials. These tutorials provide an interactive environment to step through lessons that package authors or educators have written.
Viewer
The viewer tab is used to display web content such as Shiny apps, Quarto generated web pages, or interactive htmlwidgets like plotly graphs.
Presentation
The Presentation tab is used to display HTML slides generated via Quarto’s revealjs format.